The 5 Most Important Cloud Tech Trends for 2023
With 2023, organizations are asking for more cloud computing adoption from companies, as they continue to leverage cloud technologies to drive productivity, resilience, and efficiencies. Gartner, Inc. forecasts that in 2023, worldwide public cloud spending will grow 20.7% to a total of USD 591.8 billion, up from USD 490.3 billion in 2022. The popular ‘’as-a-service” model running its servers and data centers, reduces the resource burden of a highly specialized workforce. The disruptive technology trends of the new digital world – Machine Learning (ML), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and the Internet of things (IoT), are now propelled by large-scale cloud adoption. We can expect the cloud to become a key enabler to even more of these new technologies in the future; the Metaverse, Quantum Computing Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR), and even Cloud Gaming.
Before we get into the major trends, consider the following statistics about the cloud computing market:
According to a new report by MarketsAndMarkets, the global cloud computing market size is estimated to reach USD 1,240.9 billion by 2027 from USD 545.8 billion in 2022, growing at a CAGR of 17.9 percent during the forecast period.
Below are the key trends to watch out for in 2023:
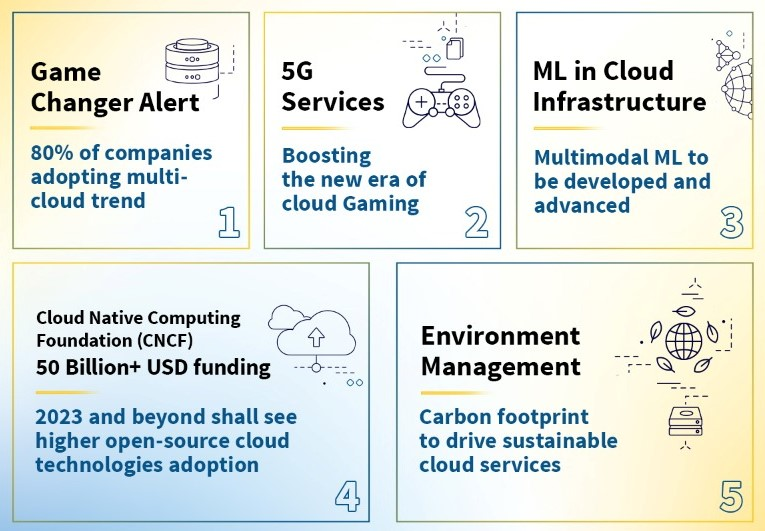
1. Multi-Cloud Is Reality, Adopt It as a Strategy
2022 paved the way for hybrid cloud technology. The year 2023 can be the year for businesses to explore the endless possibilities of diversification with multi-cloud service providers in the hybrid cloud technology space. The multi-cloud approach results in improved security, flexibility, and agility. It also contributes to the creation of redundancy, which decreases the possibility of system failures or downtime, causing a significant failure of corporate operations. Multi-cloud infrastructure adoption enables businesses to strategize business applications across cloud platforms – AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
The seemingly increased popularity of containerization is predicted to grow even more in 2023. Applications can be swiftly migrated to new platforms if service levels change or more cost-effective solutions become available from various providers. From 2020, where 70% of companies stuck to one cloud platform, to more than 80% of companies adopting to multi-cloud trend, which is a game changer for 2023.
Businesses are likely to choose multi-cloud in 2023 for the following reasons:
- Balanced benefits – private and public cloud
- Adaptability
- Cost-effectiveness
- The critical data processing capability
- Scalability
According to a GlobeNewswire article, the multi-cloud market is expected to be worth more than USD 260 billion by 2027. Over 70% of organizations worldwide have a strategy or a set infrastructure to successfully implement hybrid cloud technology.
2. Increased Investment in Cloud Resilience and Cloud Security
Cloud computing adoption is leading to the growing development of digital infrastructure. This gives a steady rise and demand for shared security responsibility and implications for numerous cloud consumption models. There can be an underlying need for security capabilities to secure cloud workloads in 2023.
2.1 Optimized and Secured Cloud Access
Cloud-native security architectures can be designed with hybrid environments in mind:
Secure cloud access with Secure = Access Services Edge (SASE), a cloud-native security platform that combines a comprehensive set of cloud-based security capabilities such as Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Next Generation firewall, Secure Web gateways, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), and DNS Security.
All of this is fully integrated with identity and access management capabilities, safeguarding access to cloud workloads from corporate branch edge, and remote mobile endpoints.
2.2 Managed Security Services and Secured Internet Access
To secure these internet connections at a reasonable price, security services can be coupled with internet connectivity services, delivering capabilities such as next-generation firewall/IPS, DNS security, and secure web access supplied as a managed platform at a low monthly subscription fee. This allows enterprises with lower security expenditures to receive effective protection services.
2.3 Zero Trust & High-level Cybersecurity Assessment
The assessment enables identifying risks in the cloud environment and mapping high-level security vulnerabilities and capabilities aimed at mitigating the identified business risks while also highlighting how the proposed security controls can be best integrated in a manner that is relevant to a digital environment and business process flows in the future.
- User trust can be maintained by effective identity and access management, which includes multifactor authentication and privilege access supplemented with real-time user access monitoring.
- Micro-segmentation with an inbuilt Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) and behavior detection features to restrict attacker lateral movement and ensure network-level least privilege access.
Data security is a major concern impeding the widespread adoption of cloud computing. A security breach can occur for a variety of reasons, including software bugs, human error, and so on. Some of the major data security challenges associated with cloud computing include the following:
- Non-authorized personnel may gain access to cloud data due to exposed APIs.
- Misconfigurations or insecure cloud infrastructure can lead to data breaches.
- Another risk associated with cloud computing is data loss. This loss can occur due to various factors, such as insufficient data backups, software corruption, natural disasters, and unintentional data deletion.
To prevent such data breaches in 2023, developers can use cloud encryption, access control, and activity monitoring.
3. The new era of Cloud Gaming – Consolidating and Innovating
The introduction of 5G services and ultra-speed networking technologies, dawns the new sky for Cloud gaming. Breakthrough innovations such as B2B game streaming services will allow developers to provide seamless streaming services to consumers.
In 2023, we can expect cloud technologies to reduce infrastructure complexity and accelerate data insights to create an excellent experience with gameplay and empower game developers for AR/VR and enhanced graphics. The facets of multi-player gaming across global geographies will again see a seemingly higher adoption as a trend boosting the market for Cloud Gaming. The Cloud gaming market is forecasted to reach a whopping USD 4 billion in 2023.
According to OpenPR – Worldwide Public Relations, the Cloud gaming market size globally reached USD 1,286.6 million in 2022. IMARC Group predicts the market to reach USD 13,581.3 million by 2028, with a Cumulated Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 47.5% during the period 2023-2028.
The global market is primarily driven by rising demand for video games and low-cost gaming solutions. In line with this, introducing a new line of games has a positive impact on market growth, as user interest in unique experiences grows. The leading players in the video gaming industry have entered the market due to the cost benefits and ease of operation. Furthermore, key companies are capitalizing on the growing popularity of video games by launching cloud gaming services to provide an affordable solution and expand the gaming market. Furthermore, the emerging trend of mobile cloud gaming is boosting the market’s prospects.
4. Make way for Artificial Intelligence (AI) + Machine Learning (ML) powered Cloud
The cloud services for 2023, shall provide more inclusivity to build AI + ML infrastructure. More data and even more algorithms require massive computing capabilities, including storage. Cloud-as-a-service model makes way for an optimized solution. Distributed networks within the cloud leverage automation to provide resources such as storage to users. Controlling and regulating data centers, and cyber security solutions leverage AI. In 2023, there can be an increasingly high ask from hyperscalers to drive innovations for their customers using the power of AI and ML.
According to a recent report by Markets and Markets, the global AI market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 36.2% during the forecast period to reach USD 407 billion by 2027. AI and machine learning can be used in conjunction with cloud computing for various applications such as digital asset management, virtual assistants, reality-as-a-service, cloud-based application security, and much more.
5. The new code for Cloud Services – Low code to No code
Low-code/no-code provides enormous benefits to digital projects by enabling rapid development in a less complex environment with built-in state-of-the-art security. Low-code to no-code platforms and tools are gaining popularity over the stereotypical computer codes. This includes building websites, and web applications, designing mobile applications, to any digital solution. These low-code/no-code solutions are looking ahead to build AI- friendly applications. These services are best provided via cloud technologies. Access it as-a-service only via the cloud.
Decoding the difference – Low code vs. No code
The demand for hyper-automation and IT modernization has increased, albeit enterprises have struggled to align with these trends due to the current scarcity of developer talent. Due to scarce resources with specialized technical skills, many IT projects are relegated to the “pending” file. As a result, operational inefficiencies persist, and time-to-market — a critical factor for businesses seeking to remain competitive — is jeopardized.
What is Low-code?
Low code is a Rapid Application Development (RAD) approach that allows for automated code generation via visual building blocks such as drag-and-drop and pull-down menu interfaces. Because of this automation, low-code users can concentrate on the differentiator rather than the common denominator of programming. Low-code is a happy medium between manual coding and no-code in that users can still add code to auto-generated code.
Business process management platforms, website, and mobile app development, cross-departmental tools like appraisal management software, integration with external plugins, and cloud-based next-gen technologies like machine-learning libraries, robotic process automation, and legacy app modernization are examples of applications that lend themselves to low-code development.
What is No-code?
No-code is also a Rapid Application Development (RAD) approach frequently regarded as a subset of the modular plug-and-play, low-code development approach. While developers do some handholding in the form of scripting or manual coding in low-code, no-code is completely hands-off, relying entirely on visual tools.
Self-service apps for business users, dashboards, mobile and web apps, content management platforms, and data pipeline builders are examples of applications suitable for no-code development. No code is used in calendar planning tools, facility management tools, and BI reporting apps with configurable columns and filters, and it is ideal for quick-to-build standalone apps, straightforward UIs, and simple automation.
Latest Blogs
Core banking platforms like Temenos Transact, FIS® Systematics, Fiserv DNA, Thought Machine,…
We are at a turning point for healthcare. The complexity of healthcare systems, strict regulations,…
Clinical trials evaluate the efficacy and safety of a new drug before it comes into the market.…
Introduction In the upstream oil and gas industry, drilling each well is a high-cost, high-risk…





