Moving from Digital Business to Cognitive Business
Many Insurance companies today are embarking on Digital Transformation rapidly, as they seek to capture the cost savings, agility, and collaboration enabled by cloud, analytics, mobile, and social technologies. However, for all the benefits of digitization and automation, enterprises find that they are still not able to incorporate new business models effectively, respond quickly to the market and disruptive forces, and scale the benefits across the enterprise.
Business imperatives are clear: Enterprises are consistently enhancing business models to improve profitability; increase revenue or get closer to customers; innovate and overcome competition and new market entrants. The availability of IT, accessible through the cloud, makes it efficient to acquire, deploy and manage IT with the result, that even the smallest players and startups (InsurTech) can achieve, with disruptive innovation and capture market share.
It is becoming clear to executives, that Digital is not the destination – Rather, it is laying the foundation for a much more profound transformation to come. This transformation is being fueled by the need to infuse decision intelligence into insurance products and processes, multi-channel interactions with customers, and heightened expectations from digitally-empowered consumers. As insurance enterprises race towards digital capability, a new business design is now gaining traction: one that marries digital business with digital intelligence, leading into the vision of a Cognitive Business.
Cognitive Business are characterized by the introduction of Cognitive capabilities into People, Process, Technology and Things, augmenting intelligence and decision making.
So what do we mean by Cognitive Applications? Cognitive Applications learn and interact naturally with people to extend what either humans or machines could do on their own. They help human experts make better decisions by penetrating the complexity of big data in all forms and variety. Cognitive Applications have technical foundations in Deep learning/Machine learning, natural language processing, reasoning and inferences and semantic contextual understanding, while leveraging relevant content and incorporation of deep subject matter expertise. This forms the basis for the foundational capabilities of Cognitive Applications implementing the capabilities of Understanding, Reasoning, Learning and Interacting with a variety of factors.
A cognitive business uses data to create knowledge and predictive insights. The business continually learns and adapts to the market forces. The ability to continually develop knowledge and insights creates a significant advantage over major competitors, and gives the ability to handle disruption and competition.
Many Insurance companies and startup companies have started to implement Cognitive applications, and are demonstrating their impact on the value chain. Established Insurance companies such as AllState and USAA have rolled out conversational applications (chatbots) for handling claims. They also help provide the right insurance products to customers. Fukoka Mutual is using claims assessment automation to replace their workforce with automation solutions. Statefarm and AXA have implemented enhanced fraud detection and dynamic pricing techniques.
Many InsurTech startups are demonstrating solutions that leverage drone images/videos to assess property damage, property appraisal using satellite pictures, end-to-end digital claims management, tracking driver behaviour to estimate policy premiums, and offering sophisticated risk assessments and fraud detection.
Leveraging the capabilities of Cognitive Applications/Artificial Intelligence, these companies are moving from the stage “So What?” to “Now What?” Experimenting with identifying use cases and incorporating Cognitive/AI capabilities into enterprise operations, insurance companies are defining the vision and roadmap to go from a ‘Foundationally Intelligent Insurer’ to an ‘Incrementally Intelligent Insurer’,and then onto an ‘Institutionally Intelligent Investor’. This journey requires strategic, functional and technical capabilities & enablers, aligned with a capability roadmap.
Strategic capabilities for a Cognitive Business include: Identification of use cases and business case(s), Data & Analytics foundational initiatives, IT/Cloud infrastructure capable of handling Cognitive workloads, Security and Governance.
Functional Enablers for a Cognitive Business include Cognitive Engagement, Cognitive Products and Services, Cognitive Process and Operations, Knowledge and Expertise Management and Cognitive Data Exploration and Discovery.
Technical Enablers for a Cognitive Business include Cognitive Data Platforms, Cognitive Data Services and Cognitive Analytics.
The combination of Strategic, Technical and Functional capabilities, along with a Capability Development Roadmap as shown below will enable an Insurance enterprise develop systematically towards becoming a Cognitive Business.
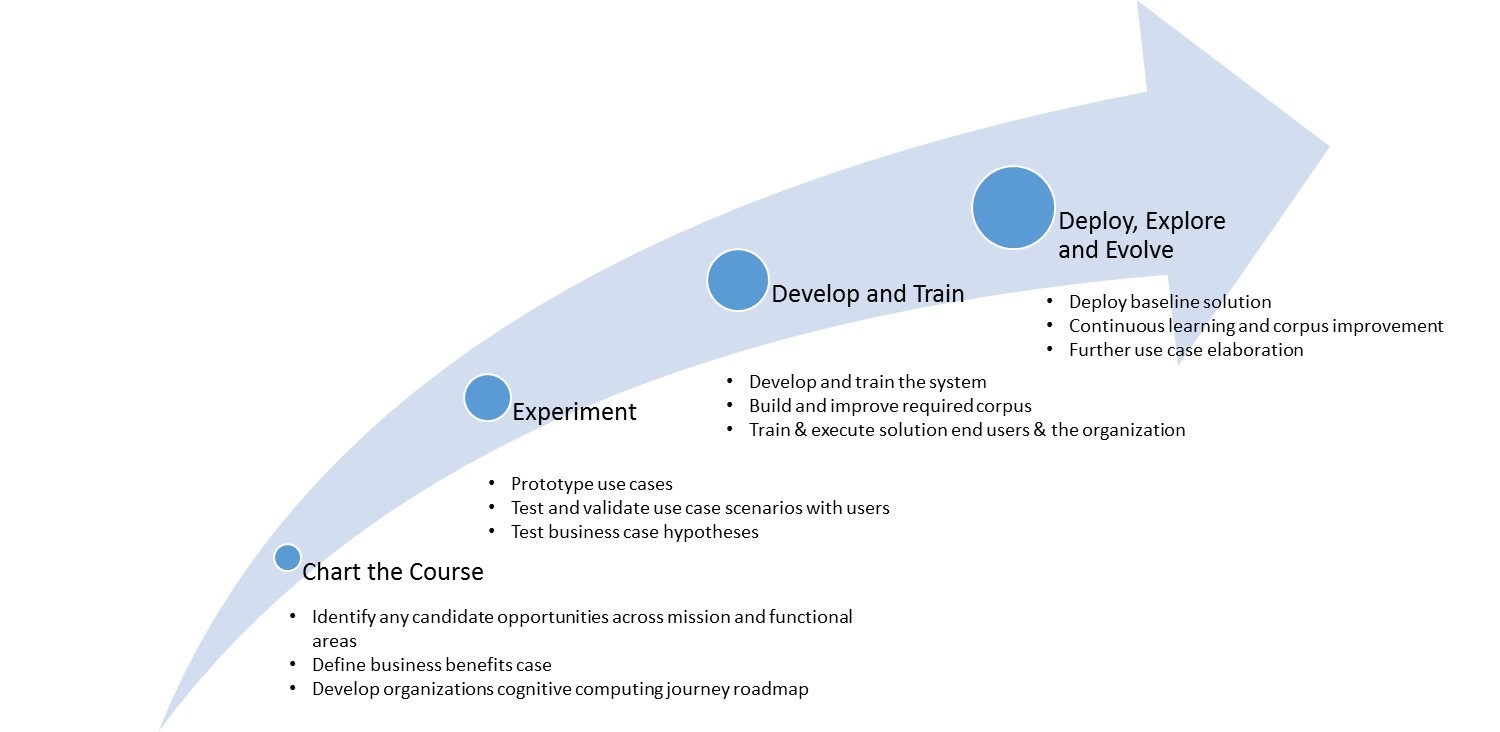
For more information, we welcome you to read the LTI whitepaper titled “Moving from a Digital Business to a Cognitive Business”.
More from Harsha Kumar Srivatsa
IBM was an early pioneer to apply Cognitive/AI technologies to the enterprise, through their…
Latest Blogs
he supply chain is a network of suppliers, factories, logistics, warehouses, distributers and…
Introduction What if training powerful AI models didn’t have to be slow, expensive, or data-hungry?…
Pharmaceutical marketing has evolved significantly with digital platforms, but strict regulations…
Leveraging the right cloud technology with appropriate strategies can lead to significant cost…




