Maximizing the Value of Data with Reverse-ETL
A decade ago, organizations struggled to bring all their data onto a single platform. Today, there are many solutions available to break down data silos and create a single source of truth. While many organizations have succeeded in centralizing their data with a data warehouse, deciding what to do with this can still be a challenge. Often, these warehouses are only used for standard visualization and reporting.
Cloud providers such as Azure, AWS, and GCP have become the nervous systems of businesses, but bringing all your data (sales, shipments, customer details, product details, etc.) together is only the first step to leverage the capabilities and scalabilities of the cloud.
Reverse-ETL fills the gap in the data cycle by helping organizations make the most of their data.
Understanding client behavior is crucial for analytics and reporting, but if that knowledge isn’t used or doesn’t reach the people who can benefit from it the most, it becomes a missed opportunity. Reverse-ETL helps ensure that valuable data is used and drives meaningful insights and actions that can help businesses stay ahead of their competition.
What is reverse-ETL?
Before jumping to reverse-ETL, let’s understand what ETL is. ETL stands for Extract-Transform-Load, which refers to the process of extracting data from various sources, transforming it as needed, and finally storing it in a data warehouse. When data size is large, it is loaded into a warehouse and only transformed when needed, rather than first being transformed and then loaded. This process is called as ELT (Extract – Load – Transform).
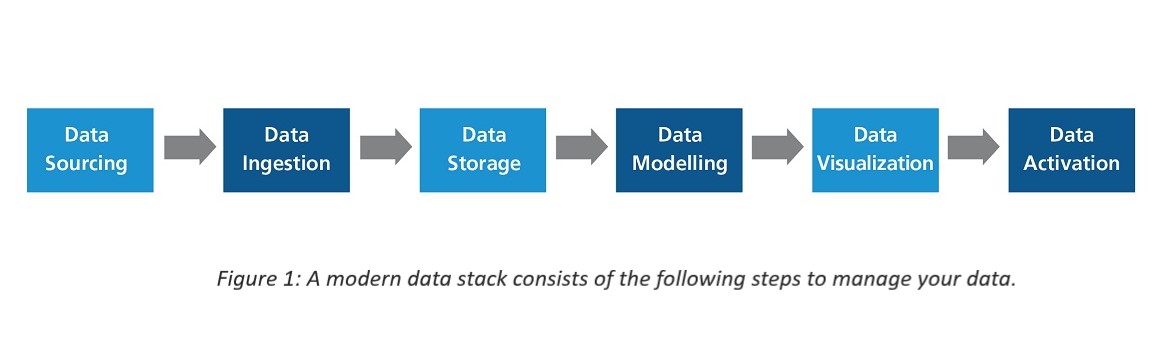
This is how data is centralized and organized. ETL is a component of the second step, or data absorption, where ETL connectors transport data from the source to the warehouse after formatting it for usage.
With this background information, let’s return to reverse-ETL. Data coming from different sources like applications, CRMs, etc. is cleaned and processed and then stored in aCRM data warehouse, which acts as a single source of truth. Data residing in your warehouse is transferred back to your applications, CRMs, tools, or any other destination that team members use daily. This process is known as reverse-ETL. To operationalize or activate this data and make it give insights of actionable value to corporate decision makers as well as the individuals who can use this data for on-the-ground jobs, it must be ingested back into a system of action like a CRM, an advertising platform, business applications. Reverse-ETL, hence, becomes a part of the data activation process.
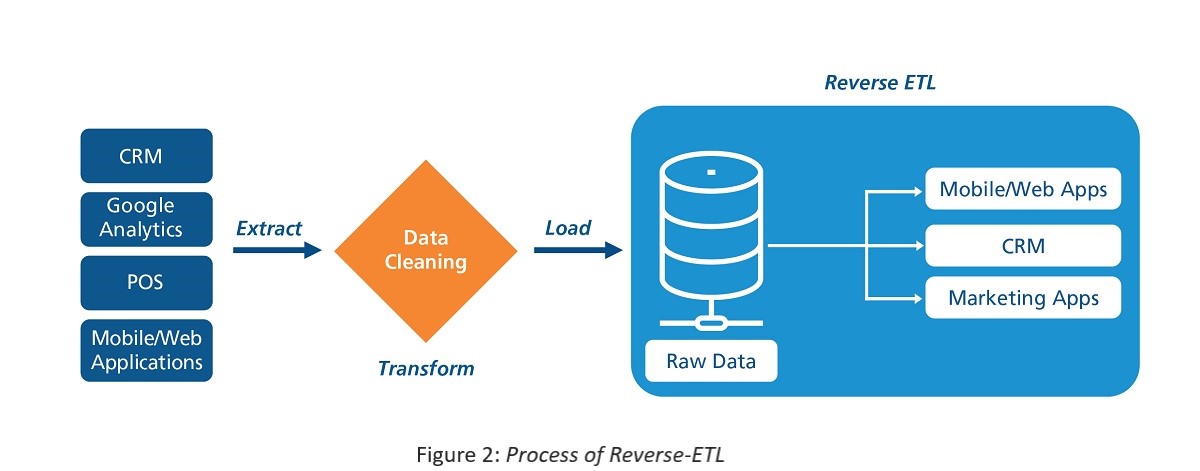
By syncing your essential business KPIs back to your tools with reverse-ETL, you can integrate data into every team’s everyday operations. The most crucial data stack phase for achieving data-driven success is this one step. The fundamental idea behind including reverse-ETL in the data stack is to operationalize analytics, which entails putting data insights into business tools so that those who have a need can quickly access them.
Let’s explore further and understand how the reverse-ETL process can be used to solve business problems.
Benefits:
Teams no longer have to go out of the way to seek data to make decisions.
The team already has the necessary data at their fingertips within the program or tools they use. Managers or salespeople don’t need to switch between CRM and BI applications to obtain the information they need. For example, salespeople don’t need to consult the warehouse or BI system to understand product usage or where a customer is in the sales funnel. They can access the information needed directly from their smartphone or CRM tool.
Data automation for streamlined workflows
Data automation with reverse-ETL can help you create more efficient and optimized operations. Reverse-ETL feeds important data points and metrics into operating systems on a predetermined schedule, which can then directly automate various workflows within those systems.
For example, imagine that your company’s sales and customer service teams use CRM daily. It’s the sales team’s job to turn freemium accounts into paying customers. Currently, account managers need to switch between CRM and BI applications to keep track of where their accounts are in the sales funnel.
With reverse-ETL, you could send product data from the warehouse to CRM and trigger an alert when a freemium account reaches a certain point in the sales funnel. This way, there’s no need for workers to constantly switch between platforms, and there’s no risk of missed opportunities. Instead, you get data-driven efficiency in terms of how work is done in timely manner.
Breaking down data silos across teams
Data silos can hinder high performance and organizational alignment, as important client data gets scattered across various technologies without a single source of truth. This leads to teams working with inconsistent information or, even worse, no data at all. If commercial teams can’t even agree on what data to begin with, how can they effectively collaborate to minimize client acquisition costs?
Data warehouses are essential for modern enterprises because they provide a secure, reliable, and cost-effective way to collect client data from all your apps. However, it’s easy for a data warehouse to become a data silo in and of itself, even though many businesses invest in them with the intention of breaking down silos.
Without reverse-ETL, your data warehouse can only store key business metrics, limiting its utility. Reverse-ETL pipelines bring data out of the warehouse and into your processes, making it accessible to everyone and visible in all the SaaS tools and apps that each team uses.
Use cases:
1. Sales
For salespeople, it might be difficult to decide which clients to prioritize. Salespeople are expected to use a variety of tools or dashboards to collect information about product consumption despite having access to a multitude of information. The sales team would be able to automatically identify leads who exhibit high levels of engagement with their product trial by syncing pertinent data into CRM via reverse ETL. It facilitates the usage of product data by the sales staff.
2. Marketing
Several teams work together in sales and marketing. It is crucial to have a strategy that enables teams to connect the many pieces of the client journey. Reverse-ETL aids with this strategy by compiling data on consumer activity throughout the whole marketing funnel.
By operationalizing client data, you may be able to answer queries like “what content or channel launched the customer journey?” Additionally, it can draw attention to details like the customer’s maximum level of involvement, the goods, or services they bought, and their overall spending. Your teams will be able to develop more individualized and successful marketing strategies if you provide them access to the whole consumer journey. Sales can nurture leads and improve conversion rates thanks to more precise information.
3. Inventory management
Only the leadership has access to stock information; the end retailer is not given access to predict data. The end retailer or counter owner can be informed when an item is about to go out of stock so they can order extra inventory before a transaction is lost.
As an illustration, a clothing manufacturer would always be analyzing data to determine which shirt styles are popularly purchased in each region. This data must, however, also be connected to the end salesman in charge of that specific region. Additionally, the planning and production teams should receive this information so they can get ready for the anticipated order. This is where reverse-ETL would be crucial in maximizing the use of the active data.
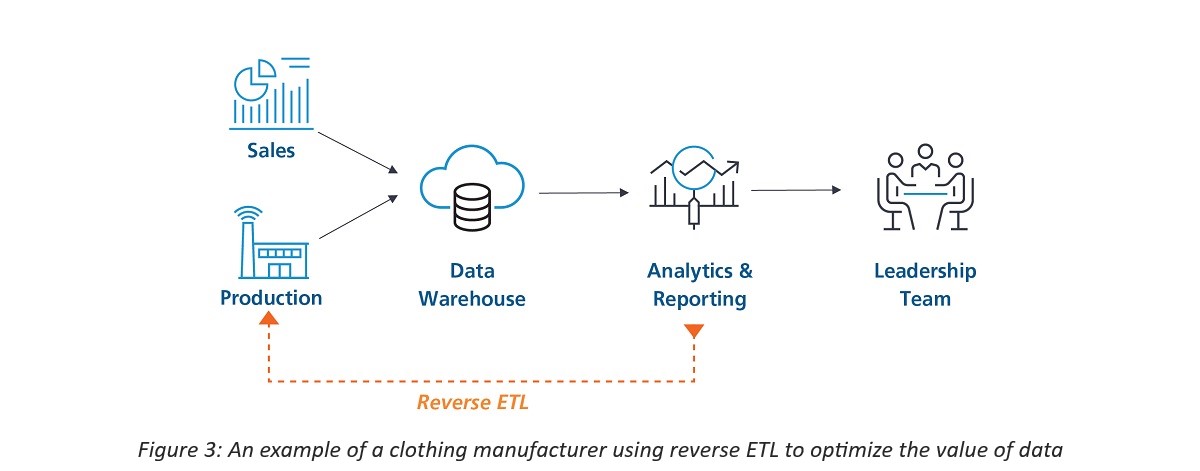
LTIMindtree has helped customers activate their data residing in data hubs. For a skincare brand, various data points were collected regarding the skin condition of customers and results obtained after using the products by beauty consultants present at counters. These data points were stored in a datahub and an analytics solution was developed to suggest or recommend products to new customers based on existing experiences. These recommendations are linked back to beauty consultants who enter skin problems into the app, based on which, they get results on which products to recommend. This way, the brand was able to serve customers better by sending back cleaned and processed data to beauty consultants.
References:
Latest Blogs
Core banking platforms like Temenos Transact, FIS® Systematics, Fiserv DNA, Thought Machine,…
We are at a turning point for healthcare. The complexity of healthcare systems, strict regulations,…
Clinical trials evaluate the efficacy and safety of a new drug before it comes into the market.…
Introduction In the upstream oil and gas industry, drilling each well is a high-cost, high-risk…




