Machine Customers: Transforming Business Interactions and Expectations – Part 2
The rise of machine customers introduces essential questions that stretch our technological imagination: Can we develop machine customers capable of true transactional autonomy? And how far are we from a future where machines operate as customers, making decisions and transactions independently? In this continuation of our blog series, we’ll dig into the state of technology today, where it’s headed, and the vital steps businesses need to prepare for this intelligent shift in AI automation in enterprises.
Is it possible to scale machine customers for real-life autonomy?
Picture a large manufacturing facility where IoT-connected machinery, inventory systems, and transportation vehicles all interact seamlessly through cloud-based connectivity. Instead of merely transmitting data back to a centralized platform, each machine becomes a customer in its own right, capable of decision-making based on performance, priorities, and even cost factors—without requiring human intervention. This shift illustrates the potential of AI for smart manufacturing, where technology can enhance operational efficiency and decision-making.
This concept isn’t just futuristic. Imagine a machine within a factory detecting a maintenance issue and autonomously prioritizing suppliers, making orders, and coordinating its upkeep based on real-time analysis of quality, cost, and delivery times. By embedding intelligence directly into these machines, they become capable of customer-like decision-making. Unlike human counterparts, who might manually weigh these factors, a machine customer can instantly analyze massive data sets with accuracy and zero distraction, streamlining processes that would otherwise require considerable oversight.
Such intelligent autonomy could transform operations by extending beyond current automated systems and introducing decision-making at scale. Machine customers[i] may soon redefine key functions in AI automation in enterprises, starting from supply chain management to customer support, digital commerce, and sales, creating efficiencies and flexibility that traditional remote handling technologies can’t match. In fact, by 2025, over a quarter of large organizations’ sales and service centers are predicted to handle requests from machine customers, reducing human involvement for routine tasks. So, could we be on the brink of a new era in customer interaction, driven by machines?
How close are we to achieving full transactional autonomy?
Today’s machine customers capture and process data through multimodal inputs, harnessing advanced neural networks that continusly learn from experience. This black box of intelligence is getting smarter with each passing day, to the day where Tesla is seen autonomously engaging with various services to optimize driving and streamline real-life operations like maintenance without the intervention of humans. This progress hints at the promise of machine customers in a B2B environment, yet there remain considerable barriers to complete autonomy.
While we’ve made strides in enabling machines to interact and transact autonomously, the road to full independence is long. Despite the progress, the current applications of AI and IoT in industries often don’t fully deliver on expectations. Machine customers still need further adaptation in decision-making abilities and more refined capabilities to interpret complex real-world scenarios. predicts that achieving full transactional autonomy across industries could take another decadei , largely due to the concerns below.
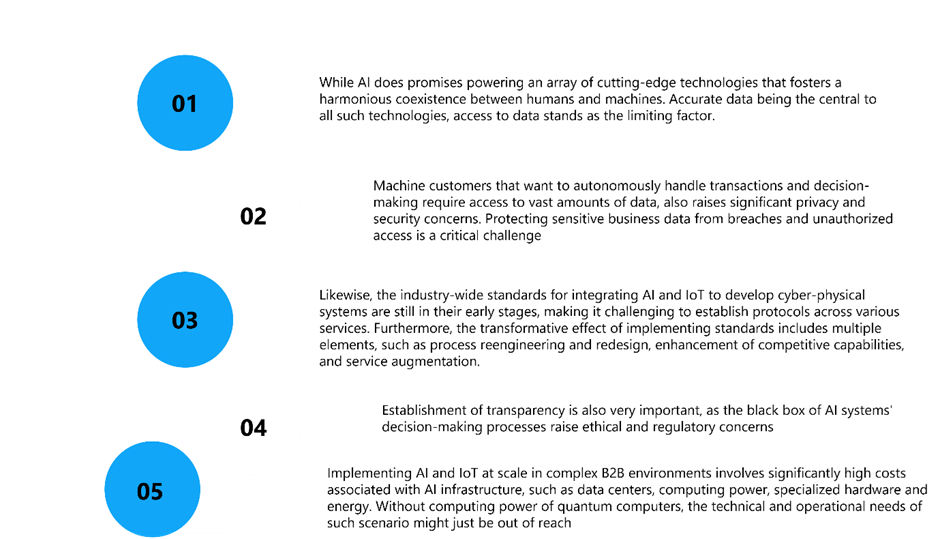
Fig 1: Challenges with implementation of Machine Customers
To move closer to this vision, machine customers must evolve beyond isolated functionality, integrating more seamlessly into business operations. But what will it take to overcome these hurdles? More than just advancements in technology, this shift requires comprehensive adaptation—from enhanced machine processing and analytics to standardized frameworks that ensure machines operate safely and reliably in business environments. Until then, these systems remain advanced assistants rather than fully autonomous actors.
Next steps: preparing for a future with machine customers
The ultimate goal for machine customers is clear: to develop AI algorithms capable of consistent performance across different business functions and deliver a dependable, integrated experience. Leading companies like Amazon, Tesla, Bosch, and Siemens have already invested in foundational technologies for AI automation in enterprises, signaling a shift toward widespread adoption. For B2B enterprises, the challenge will be to create collaborative networks that allow intelligent systems to work seamlessly together, enhancing operational performance across platforms and services.
Industry-wide collaboration will be essential to establish interoperability standards, ensuring AI systems work consistently across various sectors and can reliably support cross-industry use. Pooling resources and knowledge allows companies to offset the substantial infrastructure costs associated with machine customer adoption, making it both feasible and practical for the broader industry. Building these collaborative ecosystems will be critical to facilitate the rapid, reliable adoption of autonomous machine customers across sectors.
The development of Agentic AI and Compact Large Language Models (LLMs) represents a significant advancement in this field. These compact models, designed for efficiency and scalability, enable autonomous systems to operate on devices with limited computational resources—supporting greater flexibility in machine-driven decision-making. Though the reality of complete autonomy is still years off, investing in these emergent technologies today can position organizations at the forefront of machine customer integration as it becomes feasible.
Even though real autonomy is years away, organizations must adjust their support strategies for non-human economic actors such as machine customers. This adaptation includes:

Fig 2: Support strategies for organizational preparedness
Such efforts not only enhance the performance of machine customers but also drive innovation and competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving digital economy.
A look ahead: redefining automation and business interactions
The journey towards fully autonomous machine customers presents both challenges and enormous potential. While today’s machine customers operate within certain limits, advancements in AI and IoT signal that machines capable of independent transactions are within reach. Businesses that stay ahead of this trend—adopting the necessary technology and adapting their processes—will be well-positioned to reap the benefits of intelligent automation.
But as machine customers move closer to real transactional autonomy, questions remain. How will this shift impact traditional customer interactions? What new opportunities and challenges will arise? These are questions forward-thinking businesses should consider as they plan for the future of AI automation in enterprises.
As we edge closer to this new era, engaging in this conversation is crucial. Share your thoughts and insights by reaching out to us to learn more about how your organization can leverage these advanced technologies. Let’s work together to shape the future of autonomous transactions and redefine business interactions for the next generation.
References
[i] When machines become customers, Don Scheibenreif, Mark Raskino, Gartner: https://www.gartner.com/en/publications/when-machines-become-customers
More from Parag Mhaiske
Welcome to an era where AI is reshaping how business interact with customers. Today, AI automation…
Latest Blogs
A closer look at Kimi K2 Thinking, an open agentic model that pushes autonomy, security, and…
We live in an era where data drives every strategic shift, fuels every decision, and informs…
The Evolution of Third-Party Risk: When Trust Meets Technology Not long ago, third-party risk…
Today, media and entertainment are changing quickly. The combination of artificial intelligence,…




