Generative AI use cases in Supply chain management
Generative AI which includes technologies like natural language processing (NLP) & generative adversarial networks (GAN’s), offers several valuable use cases in supply chain processes, enabling companies to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions.
Here are some powerful use cases with examples:
Demand Forecasting:
Use Case: A retail company utilizes generative AI to forecast customer demand for its products accurately.
Example: By analyzing historical sales data, customer behavior, and market trends, the generative AI model generates precise demand forecasts for each product, helping the company optimize inventory levels and minimize stockouts.
Inventory Management:
Use Case: An electronics manufacturer employs generative AI to optimize its inventory levels based on predicted demand and supply chain constraints.
Example: By continuously analyzing factors such as sales data, lead times, and production capacities, the generative AI model generates inventory replenishment recommendations, ensuring optimal stock levels and reducing excess inventory costs.
Supply Chain Risk Management:
Use Case: An automotive company uses generative AI to identify and assess potential risks in its supply chain, such as disruptions due to natural disasters or geopolitical events.
Example: By analyzing historical supply chain data and external factors, the generative AI model identifies vulnerable areas in the supply chain, enabling the company to develop contingency plans or strategic action plan and minimize the impact of potential risks.
Transportation Optimization:
Use Case: A logistics company employs generative AI to optimize its transportation routes and reduce delivery times.
Example: By analyzing real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and delivery schedules, the generative AI model generates optimal routes for each delivery vehicle, improving efficiency and reducing transportation costs.
Procurement Optimization:
Use Case: A manufacturing company utilizes generative AI to optimize its procurement process and supplier selection.
Example: By analyzing supplier performance data, pricing trends, and historical procurement data, the generative AI model recommends the best suppliers for each product category, helping the company streamline its procurement operations and negotiate better deals. It can lead to product complexity reduction and bring economies of scale for manufacturers.
Warehouse Layout Optimization:
Use Case: A distribution company uses generative AI to optimize the layout of its warehouses for improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Example: By analyzing warehouse operations data, inventory flow patterns, and space utilization, the generative AI model generates optimal warehouse layouts, reducing travel times and maximizing storage capacity.
Predictive Maintenance:
Use Case: An equipment manufacturer employs generative AI for predictive maintenance to reduce downtime and improve equipment reliability.
Example: By analyzing sensor data and historical maintenance records, the generative AI model predicts equipment failures before they occur, allowing the manufacturer to perform maintenance proactively and avoid costly unplanned downtime.
Supplier Performance Monitoring:
Use Case: A global retailer uses generative AI to monitor and assess supplier performance continually.
Example: By analyzing supplier data, quality control metrics, and delivery performance, the generative AI model identifies potential issues and opportunities for improvement, enabling the retailer to maintain high-quality supply chain relationships.
Automated Supplier Sourcing Agreement Generation
Use case: A company regularly engages with multiple suppliers, each requiring customized sourcing agreements. Creating these agreements is a time-consuming and error-prone process that involves legal teams and procurement specialists.
Example: The AI generates the initial agreement, and legal experts review and customize it further to ensure legal compliance and alignment with specific business needs and supplier relationships. This automation process accelerates the agreement drafting process while maintaining legal integrity.
Let us try to understand this use case in application specifically with the help of process as explained below:
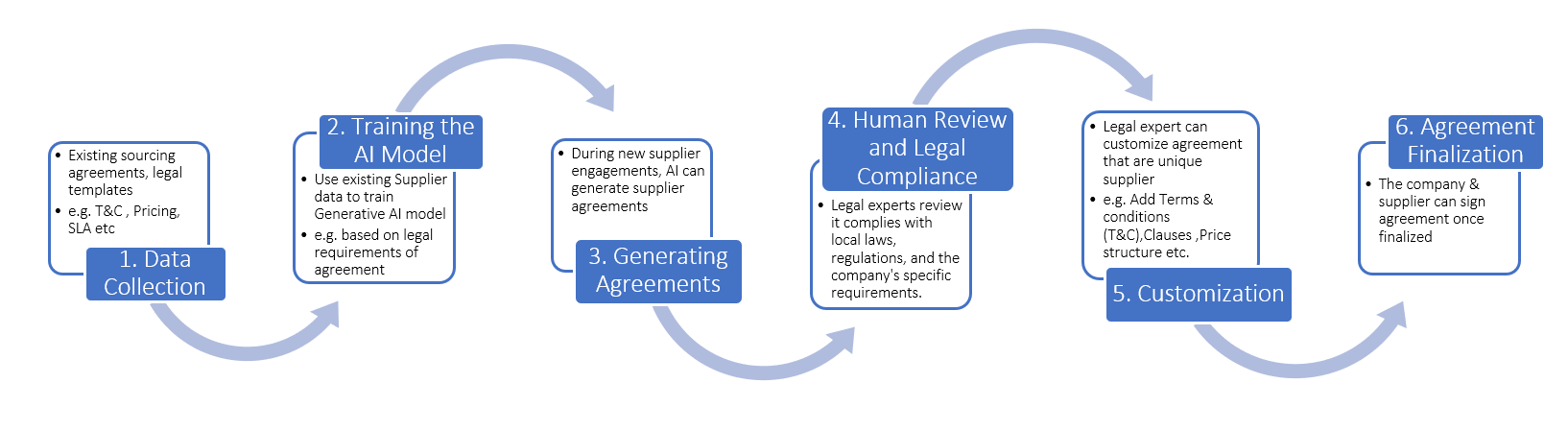
Generative ai supply chain
Let’s say a company is sourcing electronic components from a new supplier. The generative AI generates a preliminary sourcing agreement as follows:
Supplier Sourcing Agreement [Output from Gen AI]
This Agreement (“Agreement”) is entered into on [Date] by and between [Company Name] (“Buyer”) and [Supplier Name] (“Supplier”) for the supply of electronic components.
- Product Specifications
The Supplier agrees to provide the Buyer with the following electronic components according to the specifications outlined in Exhibit A.
- Pricing and Payment Terms
- The pricing for the electronic components is outlined in Exhibit B.
- Payment terms are net 30 days from the date of receipt of an invoice.
- Delivery and Lead Times
- The Supplier shall deliver the components in accordance with the delivery schedule outlined in Exhibit C.
- Any delays in delivery must be promptly communicated to the Buyer in writing.
- Quality Assurance
- The Supplier guarantees that all components meet the quality standards outlined in Exhibit D.
- In the event of defective components, the Supplier shall replace or refund them according to the terms outlined in Exhibit D.
- Termination
This Agreement may be terminated by either party with [Notice Period] days’ written notice
- Governing Law
This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of [Jurisdiction].
- Entire Agreement
This Agreement contains the entire agreement between the parties and supersedes all previous agreements and understandings.
- Signatures
This Agreement shall be effective upon the signatures of authorized representatives of both parties.
__________________________
Generative AI’s ability to generate insights from large datasets and simulate possible scenarios makes it a valuable tool in optimizing supply chain processes. These use cases demonstrate how companies can leverage generative AI to make better decisions, reduce costs, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
Latest Blogs
he supply chain is a network of suppliers, factories, logistics, warehouses, distributers and…
Introduction What if training powerful AI models didn’t have to be slow, expensive, or data-hungry?…
Pharmaceutical marketing has evolved significantly with digital platforms, but strict regulations…
Leveraging the right cloud technology with appropriate strategies can lead to significant cost…




