Future-proof your data: Uncover Backup Tape Digitization Approaches
Tape data storage has been in existence for as long as our memory serves us. However, with digital technology advancing rapidly, it is crucial to transition away from tape and embrace a more efficient way of storing data. One of the key aspects of backup modernization is phasing out legacy backup tapes. Organizations that have relied on tape backup systems for a long time are now exploring alternatives to gradually phase out tapes. They are considering tape data migration to cloud-based solutions to meet their long-term data retention needs. This blog post will explore the approaches to digitizing and phasing out LTO tapes, highlighting the benefits that each approach can bring to organizations.
Now, let’s examine the different approaches and determine the ones that suit your needs.
Before selecting an approach, it is essential to gather comprehensive information about the tape environment, which includes obtaining answers to some key questions such as:
- What type and quantity of tapes do you have?
- Which backup software platforms and versions were used to create the tapes and catalogs?
- What are the retention periods for these tapes?
Based on the answers, we can go with any of the three approaches discussed in detail here.
Approaches to tape digitization
The managed tape services option
The managed services approach involves virtualizing the existing tape backup system in the cloud. This option requires a one-time virtualization setup in the cloud environment. The vendor manages the rest of the services associated with data recovery. Data is migrated from the tapes to the cloud using proprietary software and managed as virtual tapes. When data is needed to be recovered from the legacy backup solution, the vendor does that from the virtualized tapes into a cloud bucket. When the data is not in use, it is pushed to the cold tier in the cloud, thus eliminating the need to pay higher storage costs.
Data from the tapes can either be ingested into the vendor’s cloud or the cloud subscription managed by the customer. In the latter case, the customer bears the cost of data consumption in the cloud. This approach involves end-to-end data encryption during ingestion. The tapes are managed using a secure chain of custody logistics process ensuring data security.
The managed tape services option eliminates the hassle of managing the tapes and infrastructure associated with them.
The restore option
This option uses a proprietary tape data migration system, which reads the catalog information from backup software for migrating the data. Organizations can ship the tapes to specialized vendor locations or use their current infrastructure to restore them. The vendors provide a secured chain of custody tracked logistics. The benefit of this approach is that these vendors have adequate infrastructure to restore multiple tapes at a time which makes the process faster. Besides, they also have various generations of LTO tape libraries that may not be available to the customer.
This process involves migrating the data from the tapes to the customer-managed cloud subscription. Here, the data is placed in folders based on the tapes and the catalog data. Before migration, the tapes are audited to understand the data and identify duplicate tapes. If the tapes are encrypted, the decryption keys must be shared with the vendor to recover the data.
The vendor provides catalog mapping for identifying the retrieved data in the cloud buckets. Once the data from the tapes is migrated to the cloud, the vendor hands over the reference catalog to the customer. The customer can manage data recovery using this reference catalog.
As the number of tapes increases, the complexity of recovery and the cost of this approach increases. If there is a large number of tapes involved, this option may not be viable.
The sundown approach
This approach is one of the most cost-effective solutions, as it does not involve digitizing the legacy backups from the tapes. Instead, it relies on the gradual data expiration of the existing tapes. The sundown approach usually involves the following:
- Retaining a minimum footprint of the existing backup solution to be used only for data recovery, including backup server, software, catalog, and tape library.
- Considering the backup servers are virtual machines, they can be replicated from multiple DCs onto a single DC, which can be used as a reference machine for browsing backup catalog data.
- Backup servers can be powered on whenever there is a request for data recovery and turned off when not in use.
- Whenever data needs to be recovered, the tapes can be loaded into the library, from where the data is imported on the backup server.
- The tapes can be retired as and when the data residing in the tapes expires.
This approach greatly eliminates the efforts and complexities around tape data recovery. The only downside is that maintaining a subset of the hardware and legacy software is inevitable till the expiry of the retention period. Considering the hardware may already be out of support, it becomes a challenging task to maintain hardware and software with extended/third-party support as the resolution is on best efforts basis by the vendor.
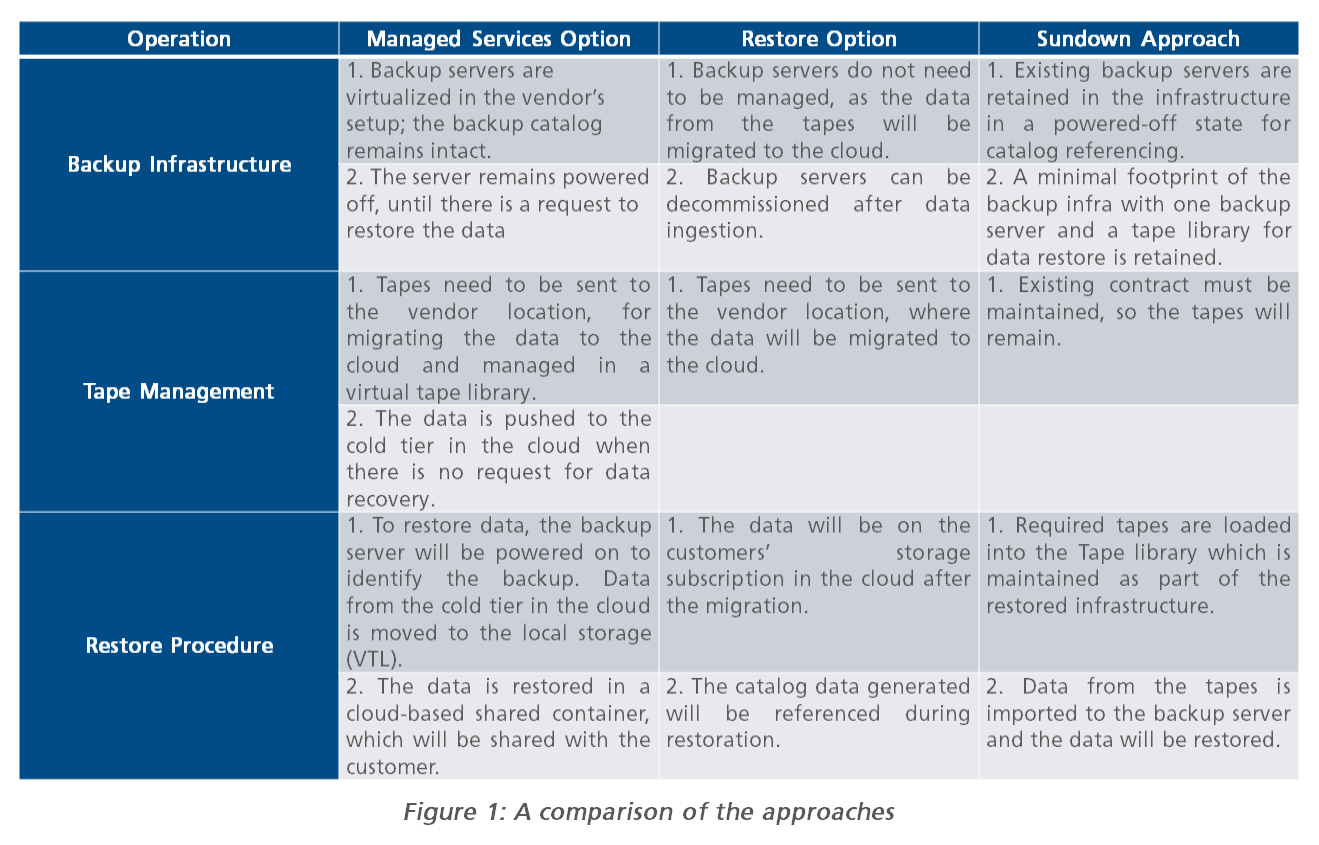
A comparison of the approaches
The table below represents the detailed comparison of all three approaches.
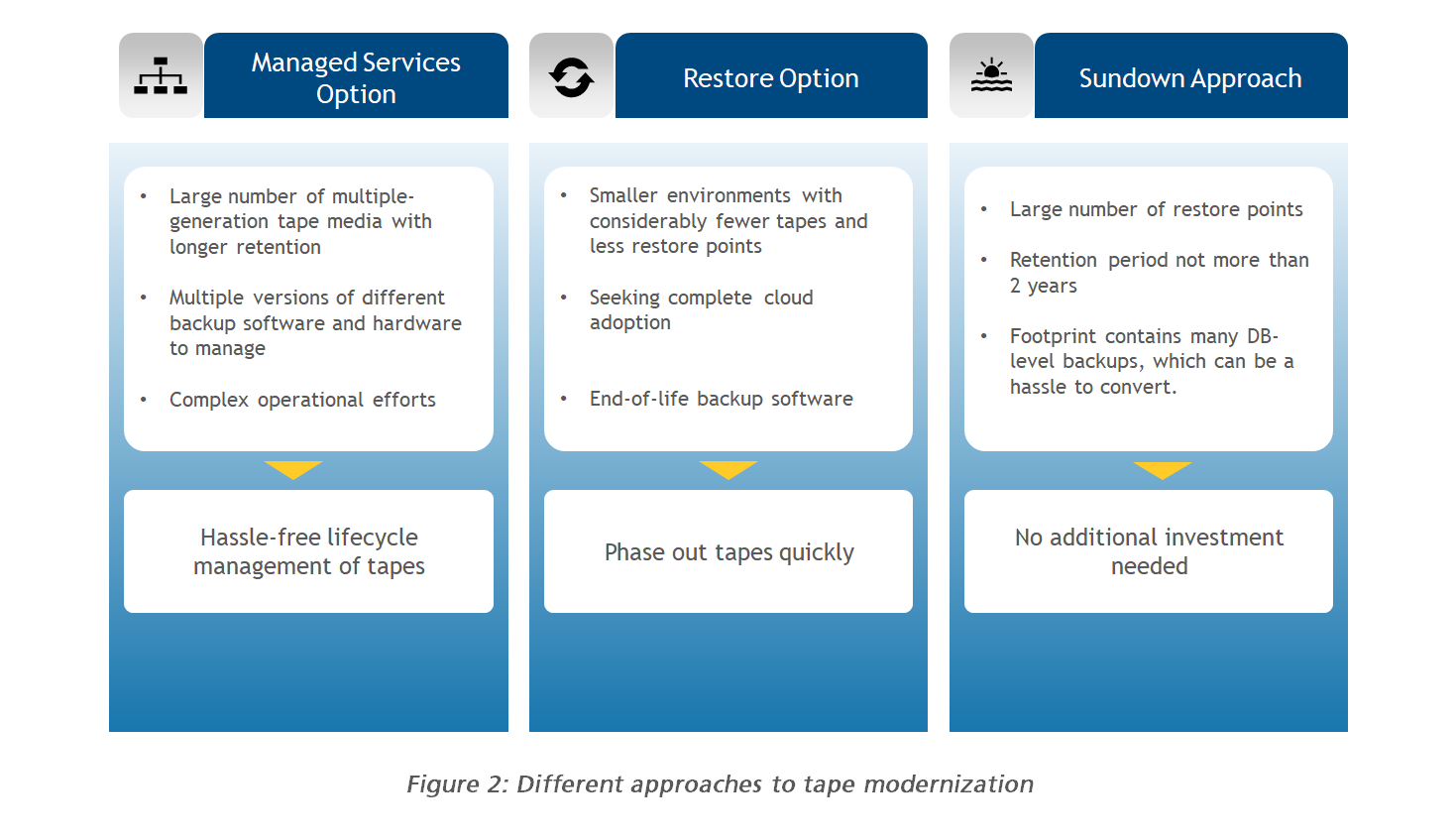
Choosing the right approach for tape digitization might vary depending on the infrastructure. The artifact below represents certain deciding factors that help choose the right option.
Legacy tapes must be destroyed for compliance and security purposes in all three approaches. The tapes must be destroyed after data migration is complete or past the data expiration date.
There are two methods of destroying tape data physically – Shredding and Degaussing. Degaussing is preferred since it leaves the media physically intact. During the process, the media is sanitized securely and rendered entirely useless. A degaussed tape is then transported for shredding.
The benefits of digitizing your data far outweigh those of using tapes, with improved security, cost-effectiveness, and scalability being just a few of them. However, migrating data from an LTO tape backup system is quite a complex process. You can choose one of the approaches or a combination of these to handle the tape digitization program. Service providers with expertise in tape digitization can help you navigate the process of phasing out the tape and fully embrace the modern backup methodology. They leverage the capabilities of a strong partner network, which helps accelerate the backup modernization process. These service providers can also help with shredding the discarded tapes by coordinating with authorized vendors to ensure compliance with regulations.
More from Amit Motiwale
In the modern world, a persisting problem for all organizations is the lurking threat of a…
Latest Blogs
Introduction What if training powerful AI models didn’t have to be slow, expensive, or data-hungry?…
Pharmaceutical marketing has evolved significantly with digital platforms, but strict regulations…
Leveraging the right cloud technology with appropriate strategies can lead to significant cost…
Introduction The financial industry drives the global economy, but its exposure to risks has…




