Enterprises Can’t Ignore Performance Testing And Engineering Of IoT Applications
Internet of things (IoT) applications are growing in popularity and use every day. As per IDC, there will be 41.6 billion connected devices worldwide by 2025. This statistic highlights the high level of penetration of IoT in our lives. Today, IoT applications provide users with real-time data to help them make quick and educated decisions.
IoT applications employ smart devices and sensors to establish Device-to-Device (D2D), Device-to-Server (D2S), and Server-to-Server (S2S) communication. This adds to the complexity of these applications. For IoT applications, it is critical to conduct rigorous testing under real-world load expectations to guarantee they can manage maximum workload with minimum effort. IoT Performance Testing and Engineering (PTE) for applications ensures that the application performance characteristics, such as scalability and availability, are maintained regardless of whatever loads or scenarios they are subjected to.
Many benefits can be gained from the effective and early PTE of IoT apps, such as ensuring that apps can handle large amounts of data, identifying potential bottlenecks or issues before they cause problems, and optimizing the IoT ecosystem’s performance. Implementing PTE early can help enterprises save time and money by avoiding unexpected outages or poor app performance while providing a better user experience. This blog will explore how performance testing and engineering of IoT apps can help businesses deliver anti-fragile business-critical IoT applications.
Why is it essential to conduct PTE of IoT Applications?
When developing an IoT application, PTE should not be an afterthought. It should be integral to the development process for a successful application launch and every major and minor release post-launch. Your IoT application must be carefully tested to ensure that it functions under all potential user scenarios, from smooth UI to availability, security, scalability, and reliability.
PTE of IoT applications allows enterprises to estimate the infrastructure capacity needed to manage heavy workloads and processing demand to evaluate the applications’ speed, responsiveness, and scalability. Additionally, PTE examines if the IoT applications are stable and maintainable over time and perform within desired load circumstances. There are certain consequences that enterprises must consider from inadequate IoT application PTE.
These are as follows:
- Significant revenue loss of brand value due to unexpected outages and poor IoT app performance. Nowadays, a little period of a system outage or inability to respond without appropriate SLAs can result in millions of dollars in revenue loss.
- The development, support, and DevOps team members’ trust in pushing any new releases or code to the production environment will be extremely low. It is challenging to estimate when the application or program will fail/stop operating or cease managing changing loads.
- Mismatch of production environment size concerning infrastructure. You will always pay more than what is required to operate the software. Lack of input from the IoT performance testing exercises results in a lack of confidence in hardware scalability.
- All performance testing issues are likely to be discovered only in a production environment.
- When a defect is reported from a production environment, it costs much more than finding and fixing it in a low-level environment. The earlier the defects are discovered, the lower the cost of repairing them.
- There will be chaos among the support, SRE, and DevOps team members until the issue is simulated, fixed, and deployed, i.e., completely resolved. The situation resembles a firefighting scenario, where teams must work around the clock until the fire goes out. This causes a lot of burnout among all team members, and imagine if this happened more frequently.
Why should enterprises invest in PTE for IoT Applications?
With rising competition in the digital realm and the requirement to rank at the top of the category, PTE has become crucial for businesses. As per Gartner, the IT Services market for IoT will represent a $58 billion opportunity in 2025. As IoT provides immense monetary value across multiple industry verticals, we believe that performance testing of IoT applications will be crucial to support processes across various verticals.
PTE of IoT applications aids in determining an IoT application’s behavior in various scenarios. An IoT app can run efficiently with a certain number of concurrent devices, but it may become problematic with thousands more during peak load. PTE will aid in determining the software application’s speed, scalability, and reliability. There are several sorts of performance tests that replicate various possible user scenarios and help to understand how apps behave.
PTE may not always reveal flaws in the IoT app. However, it will guarantee that the IoT application operates as intended, regardless of network variations, bandwidth availability, or traffic volume. PTE is a subset of the larger performance engineering picture, specifically concentrating on IoT application design and architecture performance challenges. As a result, developing and carrying out these tests is crucial for assuring the app’s stability.
An effective PTE strategy is required to identify most performance testing issues. It may be related to the database, network, software, bandwidth, or hardware. Another way to define PTE strategy is to follow industry benchmarks, which ensure that the application performs in a specified manner. As performance and scalability are important characteristics of the IoT application design and its ecosystem that need to be validated, performance testing and engineering of IoT applications would be relevant for multiple industry verticals. Some of the potential use cases are mentioned below:
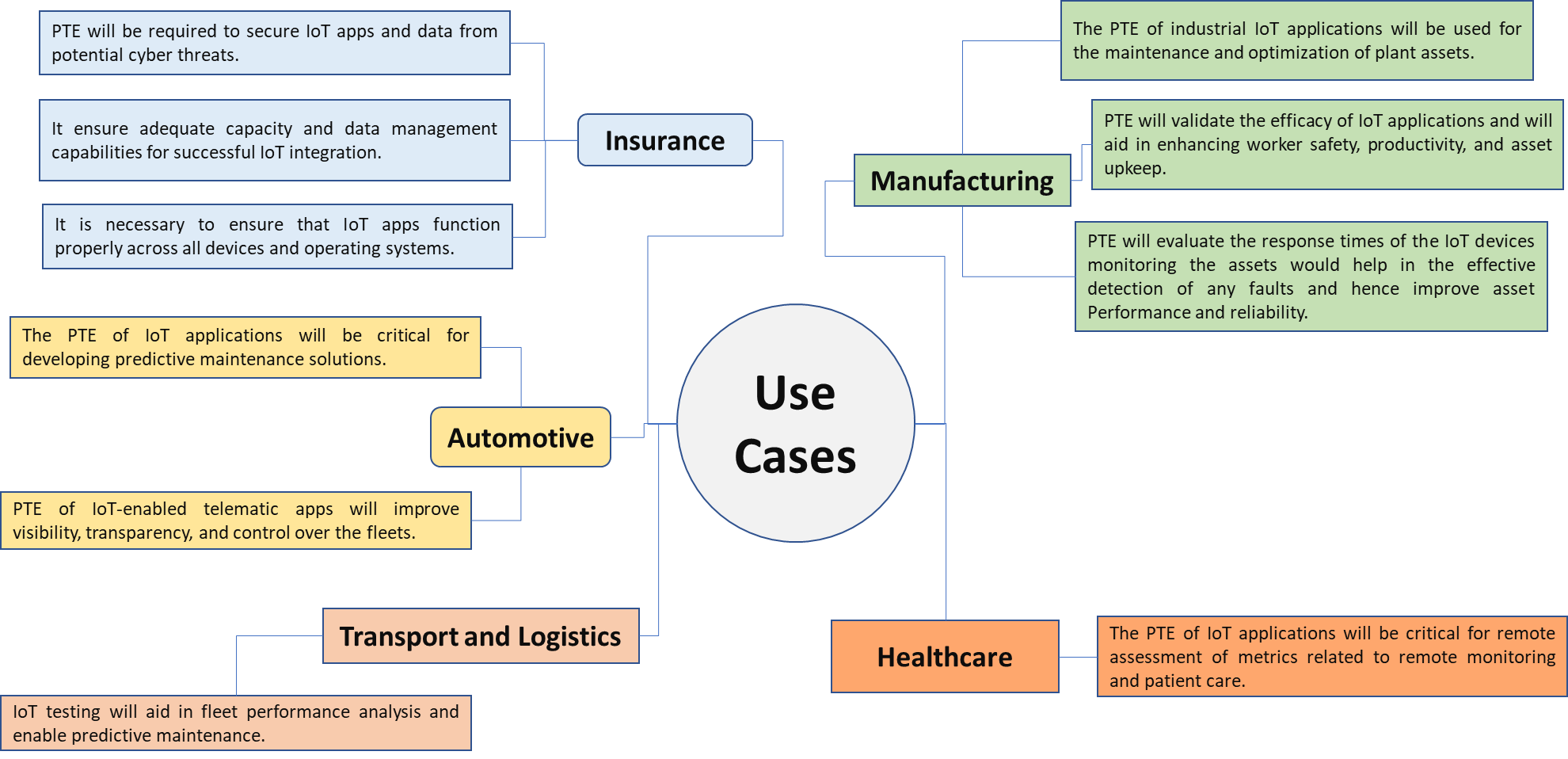
Fig.1: Potential Use Cases in Performance Testing and Engineering of IoT Application
How can PTE for IoT applications help companies realize better ROI?
Calculating the ROI of PTE of IoT applications is tricky. There are several unquantifiable advantages to IoT performance testing. These advantages are tough to translate into immediate monetary savings. However, performance testing ROI must be known to make a commercial choice.
ROI is computed by dividing the benefits of a business choice by the cost of executing that decision. ROI of PTE may be defined as a ratio of the benefits of testing to the cost of testing. The cost of testing is inversely proportional to the degree of automation. However, this cost-cutting occurs over time. In the meanwhile, automation raises the expense.
The table below depicts the progression of costs, profits, and the accompanying performance testing ROI over five years for a hypothetical case. Below assumptions have been made:
- The tool costs, person efforts, and machine costs would decline YoY with the introduction of PTE.
- With early PTE introduced, there would be initially approximately 10% fewer failures, which would subsequently go up to 20%, and hence fewer costs associated with fixing them.
- Application maintenance costs would be 70% of the revenue.
- With stable and high-quality applications running, organizations can increase their revenue by 7-8%.
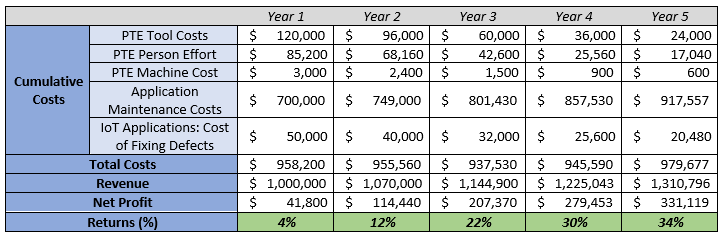
Table: ROI Implications on introducing Performance Testing and Engineering
The below figure shows the costs, profits, and the ROI graphically over the five years.
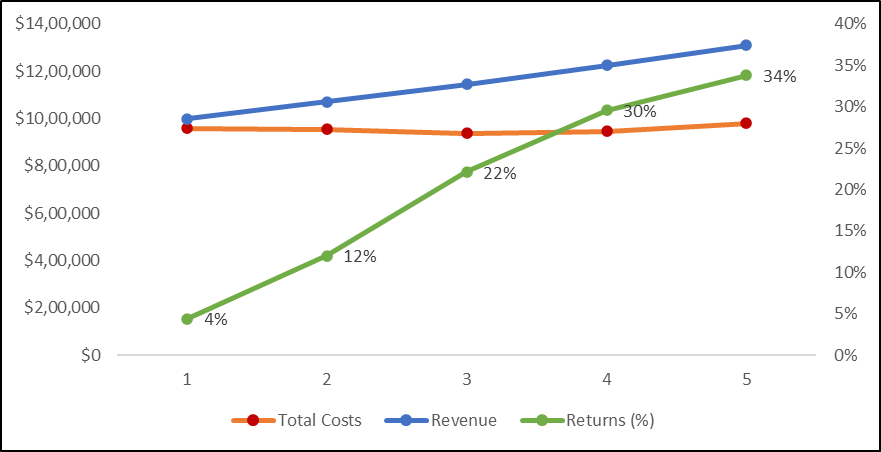
Fig.2: RoI progression over a 5-year period
Conclusion
There is a considerable need for evaluating and certifying IoT applications for their performance, scalability, and resilience. Very few service providers provide PTE services for IoT applications. Building robust specialized IoT performance testing and engineering services might offer several opportunities for a services-based organization. It will allow businesses to support multiple protocols, emulate networks, and support cloud-based load generation, which is currently difficult to do with traditional methodologies. To develop these capabilities, organizations must concentrate on the following pointers:
- Collaborate with testing and performance engineers to identify PTE use cases where IoT application performance tools are yet to be realized.
- Calculate your peak load between D2D, D2S, and S2S data transfer at any time.
- Develop test cases for your objects, and define typical and unusual usage scenarios.
- Determine whether your application employs any proprietary protocols and develop a testing tool that will enable you to rapidly and efficiently performance-test these protocols.
It’s a matter of time until the PTE of IoT applications becomes standard practice. You can ensure the availability and performance of IoT applications more quickly if you take a systematic approach to creating and implementing a testing plan.
More from Hakimuddin Bawangaonwala
In today's interconnected application ecosystem, data security and privacy are more significant…
This decade has been dominated by AI advancements. Generative AI took center stage in late…
A new generation of smart, intelligent, and interactive workspace technology has emerged over…
Introducing the future of AI - generative AI We are in the golden period of AI (Artificial…
Latest Blogs
Introduction What if training powerful AI models didn’t have to be slow, expensive, or data-hungry?…
Pharmaceutical marketing has evolved significantly with digital platforms, but strict regulations…
Leveraging the right cloud technology with appropriate strategies can lead to significant cost…
Introduction The financial industry drives the global economy, but its exposure to risks has…




