Enhancing Efficiency in Supply Chain and Logistics with AI Agents
he supply chain is a network of suppliers, factories, logistics, warehouses, distributers and retailers through which raw material is acquired, transformed, transported and sold to customers. Ensuring smooth coordination across all of these entities is essential for operational continuity, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Whereas logistics refers to the planning and coordination of transportation, storage and delivery activities across the supply chain. It includes functions such as warehousing, inventory management, order fulfilment and customer service. These logistic operations serve as the backbone of an efficient supply chain.
With today’s supply chains growing more complex and dynamic, businesses are turning to intelligent automation to improve efficiency. This is where AI agents come in. They are autonomous, goal-driven systems that can analyse data, make decisions and take actions across various supply chain functions.
But how does the supply chain function?
In a typical supply chain, goods move through a network of suppliers, production hubs, warehouses and distribution centers before reaching end-customers. The diagram below illustrates the flow (see figure 1).
Real-time data exchange across each note is critical to ensure visibility, coordination, and timely execution, A lean supply chain focuses on selecting the right suppliers, optimizing transportation and warehousing, and applying just-in-time (JIT) practices to reduce delays, inefficiencies, and operational waste.
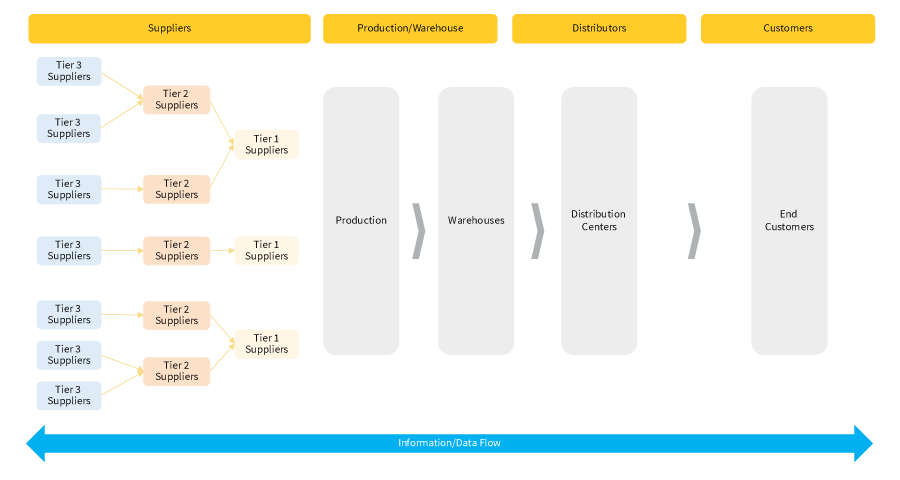
Figure 1: Supply chain flow
How AI agents are reshaping supply chain efficiency
As supply chain grows more dynamic and data-intensive, AI agents are emerging as a powerful force to drive real-time decision-making and intelligent automation.
These software-based agents go beyond traditional AI systems by combining machine learning, natural language processing (NLP) and visual recognition with the ability to independently analyse data, take contextual actions, and continuously improve outcomes. From optimizing operations and minimizing costs to enhancing customer experience, AI agents are transforming every link in the supply chain.
According to Gartner, leading supply chain organizations invest in AI and machine learning technologies at more than twice the rate of lower-performing peers to improve forecasting accuracy, resilience, and delivery performance.AI agents explained
AI agents are autonomous software applications capable of making decisions and taking actions without constant human intervention. Unlike typical Gen AI models, AI agents are designed to connect with external systems via APIs, web services, and databases to gather contextual data, reason independently, and act based on predefined goals.
By analysing real-time data and recognizing patterns, AI agents can automate routine tasks, assess risks, optimize resources, and provide contextual recommendations. Their reasoning capabilities help reduce bias and improve objectivity in complex decisions. According to a Google whitepaper, an AI agent combines reasoning, logic, and access to external data, connected to a generative model, to function autonomously. Google has launched a general agent architecture and components as shown below:
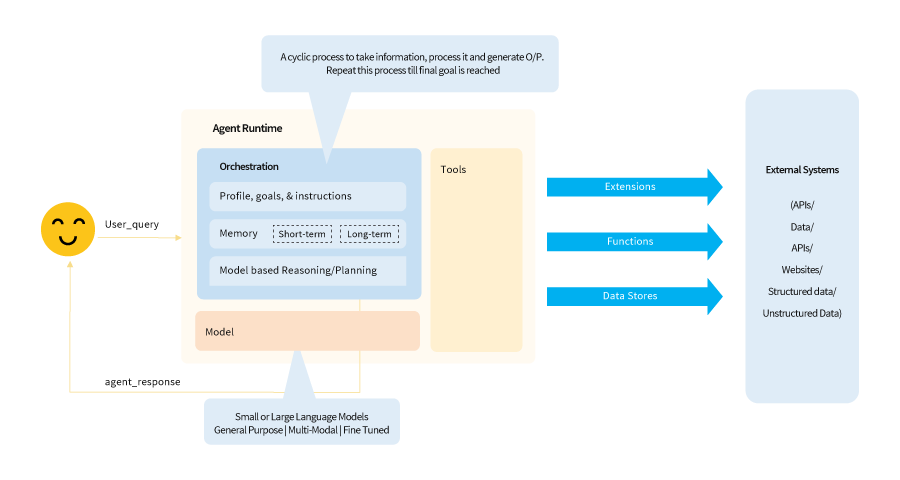
Figure 2: Google general agent architecture and components
Google’s agent architecture includes a feedback loop for continuous processing and external data integration, enabling autonomous decision-making.
The agent architecture is made up of three key layers – model, orchestration, and tools. All three work together to enable continuous goal-seeking behaviour.
- Model: Refers to any small or large language model capable of reasoning and follow any logic framework such as ReAct, Chain-of-Thought, etc. For ideal performance of the model, it should be trained on the problems you plan to solve using this agent and with the tools that will be used during this process.
- Orchestration layer: This layer contains a cyclic process to digest incoming data, apply reasoning and make contextual decisions. This decision can be final or an intermediate one – which can be used as input for next cycle. The agent iteratively refines decisions through this cycle until a goal is achieved.
- Tools: Most of foundational AI models are restricted by their ability to connect with external data. The agent helps in bridging this gap by letting models connect to external data using tools (as shown in figure above).
Tools are mechanisms that bridge internal model reasoning with the external environment. For example, an AI logistics agent can connect to weather API to reroute shipments in case of major weather disruptions. Tools fall under these categories, such as extensions, functions, and data stores.
Glossary: Extensions are standardized interfaces that allow agents to bridge the gap between APIs and agent seamlessly, while functions are self-contained modules of code that accomplish specific tasks. Data stores provide agents with access to updated information from various sources, such as websites, structured data (Word docs, PDFs), and unstructured data (HTML, TXT). These tools collectively enable agents to get real-time information and make informed decisions
Key capabilities of AI agents in supply chain and logistics
- Demand forecasting & inventory management: AI agents analyze historical data, market trends and external inputs to forecast demand and maintain Just-in-time inventory levels. This helps reduce warehouse space, optimize inventory costs, and improve cash flow. Integrating AI agents with ERP, IoT, and warehouse management systems ensures seamless orchestrations across supply and inventory functions.
- Route optimization: AI can access APIs related to weather, traffic, and geopolitical events to suggest optimal delivery routes. This improves delivery predictability and reduce transportation costs.
- Predictive maintenance: AI agents monitor machine performance in real time to predict potential failures. This enables proactive repairs, reduces downtime, and prevents supply chain disruptions.
- Customer service automation: AI agents assist in customer service by automating queries such as shipment tracking and return requests. They also help prioritize support tickets and streamline resolution workflows.
- Supplier performance: AI agents can monitor suppliers’ performance metric such as delivery timelines, compliance scores, and quality benchmarks. This helps maintain SLAs and supports proactive supplier management.
Utilizing Google’s agent framework for a transport use case:
To address various supply chain issues using AI agents, business use cases should be grouped into logical categories such as customer service, demand forecasting, transportation, logistics, and return management, each category can be handled by a specialized AI agent trained on specific sample datasets.
The following diagram illustrates a basic route selection problem addressed by an AI transport agent built on Google’s cognitive agent architecture (See figure 3).
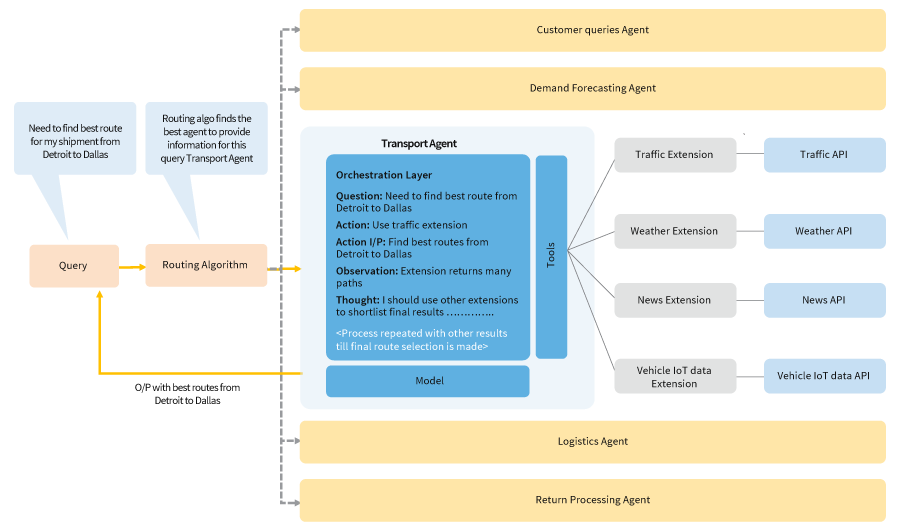
Figure 3: AI agent framework applied to a transport use case for real-time route planning.
Tips for using AI agents in Supply Chain and Logistics
- Keep a human in the loop for high use cases such as returns processing.
- Use proprietary enterprise data to train each agent for better contextual accuracy.
- Launch an AI literacy program to encourage cross-functional adoption.
- Define SLAs to track outcomes and continuously improve agent performance.
Conclusion
AI agents are revolutionizing supply chain and logistics by enabling more efficient, agile, and customer-centric operations.
- Optimize operations – AI improves forecasting, inventory control, and route planning to streamline workflows.
- Reduce costs – Automation minimizes human error and reduce transportation, storage and labour overheads.
- Enhance customer experience – AI enables real-time tracking, smarter returns processing, and proactive support.
By applying Google’s AI agent cognitive architecture, such as the framework outlined in Google’s transport use case whitepaper, companies can unlock real-time decision-making, predictive analytics and self-learning capabilities. This helps them stay resilient, innovative, and competitive in today’s dynamic supply chain environment.
References:
- Gartner Says Top Supply Chain Organizations are Using AI to Optimize Processes at More Than Twice the Rate of Low Performing Peers
- Google Agents Whitepaper written by Julia Wiesinger, Patrick Marlow and Vladimir Vuskovic
Latest Blogs
Introduction What if training powerful AI models didn’t have to be slow, expensive, or data-hungry?…
Pharmaceutical marketing has evolved significantly with digital platforms, but strict regulations…
Leveraging the right cloud technology with appropriate strategies can lead to significant cost…
Introduction The financial industry drives the global economy, but its exposure to risks has…




