Driving Innovation and Sustainability: The Future of Quality Engineering (QE)
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the demand for high-quality software has never been greater.
Globally, many organizations are aware of their IT footprint. However only few of them have a comprehensive, sustainable IT strategy with well-defined goals and target timelines.
Enterprises across industries are not only striving to meet customer expectations and adhere to stringent quality standards. However, as the digital age improves, there is a growing need to integrate sustainability into QE practices.
Sustainability is to recognize the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic systems to manage finite nature’s resources for a greener tomorrow.
In this blog post, we will explore the intersection of QE and sustainability, key concepts, challenges, and innovative solutions that are shaping the future of Quality engineering.
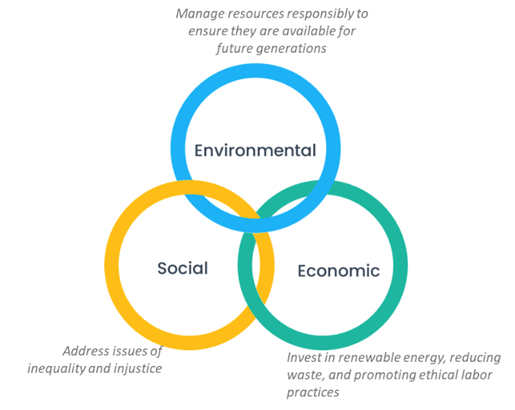
Figure 1: Three circles of sustainability
Factors contributing to unsustainability in IT and QE
While the IT industry and QE within the IT industry have the potential to support sustainability efforts, they also face challenges and contribute to unsustainability in several areas:
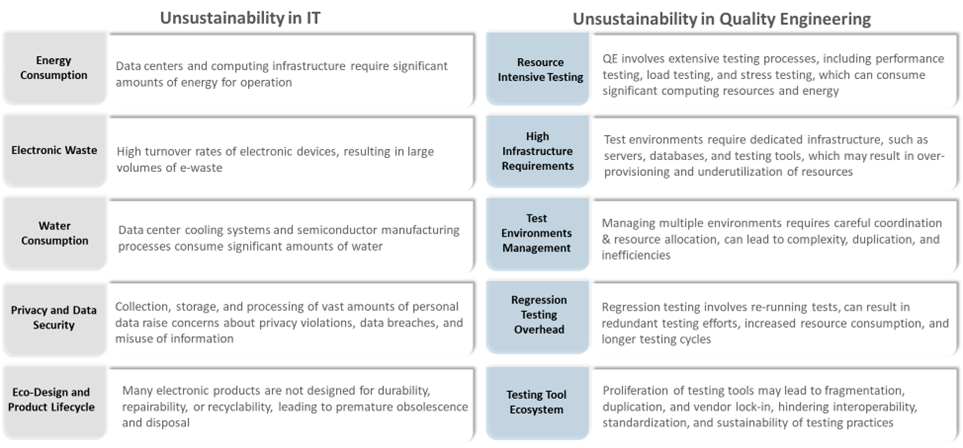
Figure 2: Unsustainability in the IT and QE
Business opportunities in IT and QE
Enterprise IT contributes significantly to the world’s carbon footprint, and interestingly, a lack of tools and expertise in this area undermines the adoption and deployment of solutions. Sustainability is not a priority for most organizations, but they can significantly contribute to building tools, technologies, solutions, and frameworks for sustainable practices.
Sustainable practices in QE
Enterprises can implement a variety of sustainable practices to enhance their QE practices. These include leveraging green testing infrastructure to minimize energy consumption, adopting cloud-based testing solutions to reduce resource usage, implementing test automation tools to improve efficiency, and prioritizing sustainable test data management practices to minimize waste. By integrating these practices into QE, organizations can not only reduce their environmental footprint but also drive innovation and efficiency. Some of the sustainable practices in QE are:
- Green testing infrastructure
Consolidate servers, leverage virtualization, and adopt energy-saving technologies such as dynamic power management and server consolidation to optimize testing infrastructure for energy efficiency.
- Cloud-based testing
Utilize cloud computing for testing environments to scale resources based on demand, minimize hardware requirements, and reduce energy consumption associated with maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
- Test automation
Embrace test automation to reduce manual testing effort, improve efficiency, and minimize resource consumption by executing tests through tools.
- Efficient testing processes
Streamline testing processes, prioritize critical tests, and eliminate redundant or unnecessary testing to reduce testing time, resource usage, and environmental impact while maintaining quality standards.
- Environmentally-friendly Management (TDM)
Implement sustainable practices for test data management, including data anonymization, data masking, and data virtualization, to minimize storage requirements, improve data privacy, and reduce environmental impact.
- Carbon-neutral testing environments
Offset carbon emissions associated with testing activities by investing in renewable energy projects or purchasing carbon credits to achieve carbon neutrality for testing operations.
- Green procurement practices
Source testing tools, software licenses, and hardware equipment from vendors with strong environmental credentials, such as energy-efficient products, eco-friendly packaging, and sustainable supply chain practices.
- Training and awareness
Educate QE teams about sustainability principles, practices, and tools through training sessions, workshops, and knowledge-sharing initiatives to raise awareness and foster a culture of sustainability.
- Continuous improvement and measurement
Implement metrics, KPIs, and dashboards to monitor sustainability performance in QE processes, track resource usage, identify areas for improvement, and measure progress over time.
- Collaboration with sustainability teams
Collaborate with sustainability teams or departments to align quality engineering practices with broader sustainability goals, share best practices, and leverage synergies between quality and sustainability initiatives.By integrating sustainability practices into quality engineering processes, organizations can reduce environmental impact, enhance operational efficiency, and contribute to broader sustainability objectives while maintaining high-quality standards in software development and delivery. Below are some of the applicable use cases across STLC:
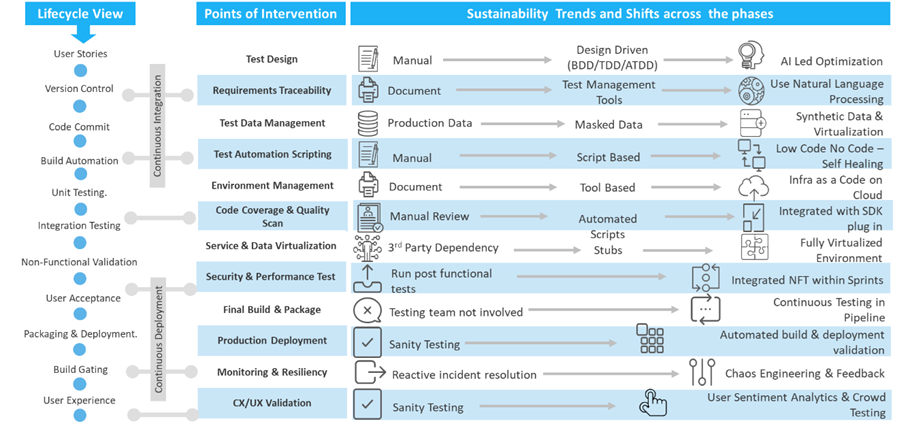
Figure 3: Sustainable use cases across software test lifecycle
Exploring new ideas and innovations
In addition to leveraging existing tools and frameworks, organizations can explore new ideas and innovations to further enhance their sustainable QE efforts. For example, developing green testing dashboards, carbon footprint calculators, and sustainable TDM platforms can provide valuable insights into environmental impact and guide efforts to reduce emissions and waste. Furthermore, certification programs and community platforms can help foster collaboration and knowledge sharing among practitioners interested in sustainable QE practices.
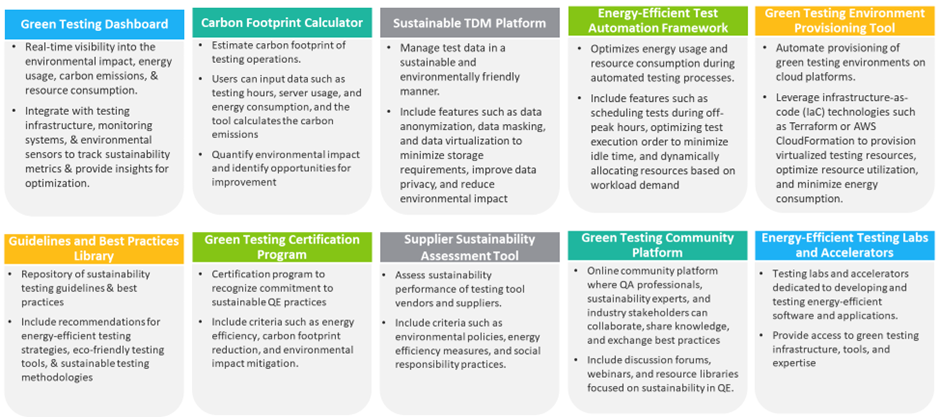
Figure 4: Sustainable frameworks, tools, solutions, and methodologies.
Sustainable QE offerings
Developing sustainable QE solutions should align with organizational strategy. Through tailored sustainable QE offerings, a new standard in the industry could be set, where every test conducted contributes to a greener and more sustainable future. Below are a few ideas that can be developed into full-fledged service offerings to improve the future of quality engineering:
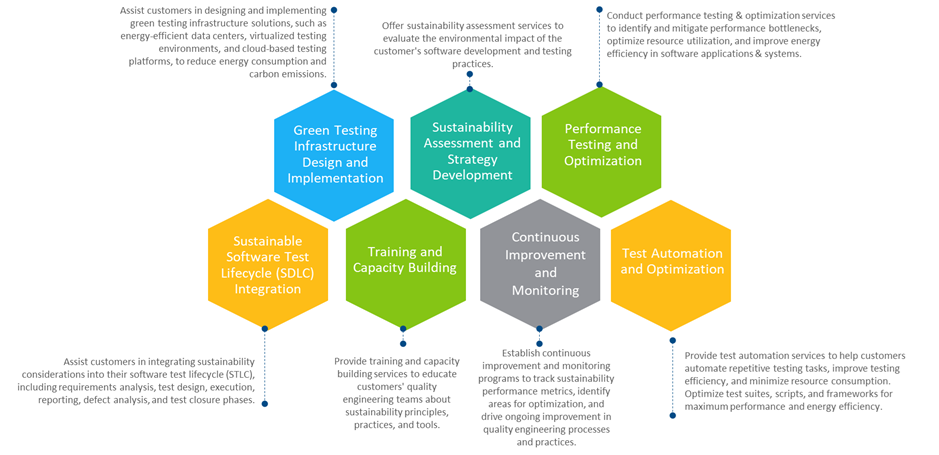
Figure 5: Sustainable QE service offerings
Implementation approach
Designing and implementing sustainable quality engineering (QE) practices involves a structured approach that integrates sustainability considerations into every phase of the software development lifecycle. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to design and implement sustainable engineering practices:
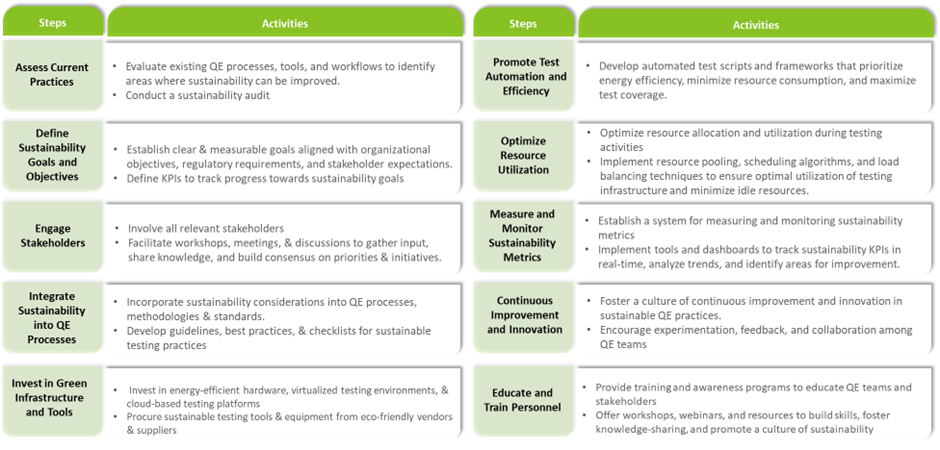
Figure 6:Implementation approach for sustainable QE
Stakeholders involved
Designing and implementing sustainable engineering practices involves collaboration among various stakeholders across the organization. Here are the key stakeholders who should be involved:
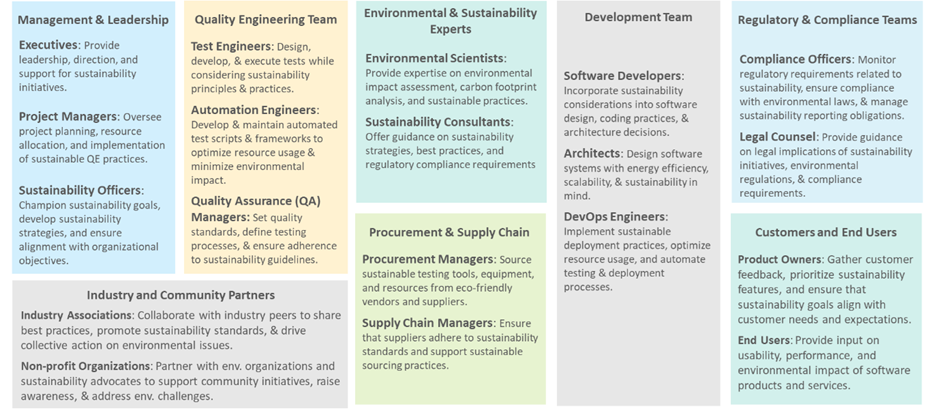
Figure 7: Stakeholders involved in sustainable QE
Implementation of sustainable QE practices
Sustainable quality engineering (QE) practices can be implemented throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC), but their applicability and emphasis may vary depending on factors such as project requirements, organizational priorities, and resource constraints. Here’s a breakdown of when sustainable QE practices can be implemented:
- Throughout the SDLC: Sustainable QE practices can and should be integrated into various phases of the SDLC, including requirements analysis, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
- During special intervention points:
- Requirements gathering: Ensure that sustainability requirements are explicitly captured during the initial requirements gathering phase.
- Design and architecture: Incorporate sustainability considerations into system design and architecture decisions, such as selecting energy-efficient technologies, optimizing resource usage, and designing for scalability and sustainability.
- Testing and validation: Perform sustainability-focused testing and validation activities to assess the environmental impact of systems.
- Continuous improvement: Implement continuous improvement processes to monitor sustainability metrics, track performance over time, and identify opportunities for optimization throughout the software development lifecycle.
- As part of organizational culture: Sustainable QE practices should ideally be ingrained as part of the organizational culture, with stakeholders at all levels actively promoting and supporting sustainability initiatives.
- During critical project milestones: Organizations may choose to emphasize sustainable QE practices during critical project milestones, such as product releases, major updates, or regulatory compliance deadlines.
Benefits of sustainable QE practices
Sustainable QE is essential for organizations seeking to balance economic prosperity with environmental responsibility, comply with regulations, mitigate risks, and enhance their competitive position in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
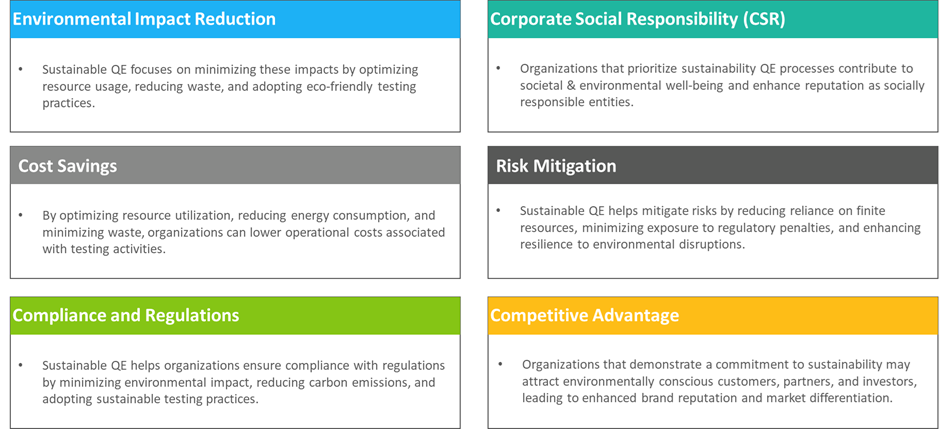
Figure 8: Sustainable QE benefits
As organizations continue to prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility, the role of quality engineering becomes increasingly critical. By integrating sustainable practices into QE processes, organizations can not only reduce their environmental footprint but also drive innovation, efficiency, and long-term value. Through a collective commitment to sustainability, we can create a brighter future for generations to come. Together, let’s embrace the challenge of driving innovation and sustainability in quality engineering, paving the way for a greener and more prosperous world.
Request a free consulting session to assess the sustainability of your Quality Engineering practices by contacting us at qes@ltimindtree.com
Let’s drive impactful results together!
References:
Sustainable Test-Driven Development, PMI:
ISO 14001:2015, ISO, September 2015:
https://www.iso.org/standard/60857.html
Latest Blogs
A closer look at Kimi K2 Thinking, an open agentic model that pushes autonomy, security, and…
We live in an era where data drives every strategic shift, fuels every decision, and informs…
The Evolution of Third-Party Risk: When Trust Meets Technology Not long ago, third-party risk…
Today, media and entertainment are changing quickly. The combination of artificial intelligence,…




