Decarbonization in Oil and Gas value chain
Decarbonization and Digital Solutions Accelerating Net-Zero in the Oil and Gas Industry
Decarbonization is helping enterprises to accelerate and achieve Net-Zero in the oil and gas industry. Our blog dwells upon this subject and details decarbonization and the Net-Zero movement in this sector.
Like all other industries, the petroleum industry is taking significant steps to move to a carbon-neutral world. The selection of the right digital technology/solution will complement these efforts. This paper focuses on a few areas, specifically in the oil and gas value chain, and potential digital solutions that can be adopted to accelerate the journey toward Net-Zero emission.
What is Decarbonization?
Decarbonization, simply put, means preventing or lowering the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere or removing the carbon dioxide from the air through various means. Though the word refers to carbon, it is used in a broader sense to cover all greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. GHG includes other gases apart from carbon, such as methane, nitrous oxides, and other industrial gases. But the carbon contribution to GHG is much larger if the volume is considered, hence the word “decarbonization.”
Net-Zero movement
With the wide adoption of the historic Paris Agreement by almost 200 countries, there has been a concerted movement in the industry to reduce carbon footprint and reach carbon neutrality (Net-Zero) by 2050.
These industries predominantly include agriculture, manufacturing, transportation, petroleum, construction, electricity, and heat production, among others.
GHG emissions sources and intensity may vary with industry processes; however, some measures taken to reduce the footprint are standard across industries. Most focus on reducing GHG emissions from existing operations, capturing carbon emitted from various processes, switching to renewable energy sources, focusing on energy efficiency, and increasing the use of carbon offsets.
The oil and gas industry is no different.
Carbon footprint in the oil and gas value chain
GHG emissions come from various sources across the oil and gas value chain, from conventional and unconventional production to collecting and processing oil/gas and its transmission and distribution to consumers.
Directly and indirectly, the oil and gas industry accounts for 42 percent of global emissions1.
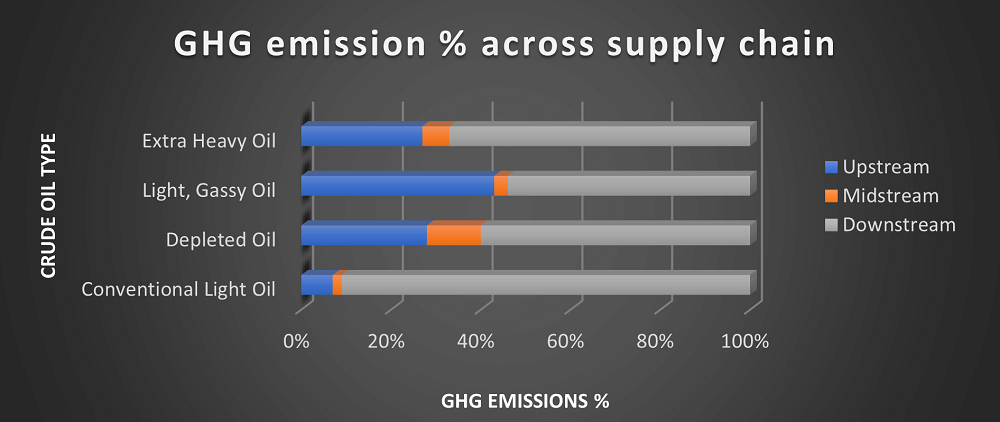
The following chart represents the percentage of GHG emissions across Upstream, Midstream, and Downstream for four representative types of crude oil2.
The following activities are significant contributors to carbon and methane emissions throughout the oil and gas value chain:
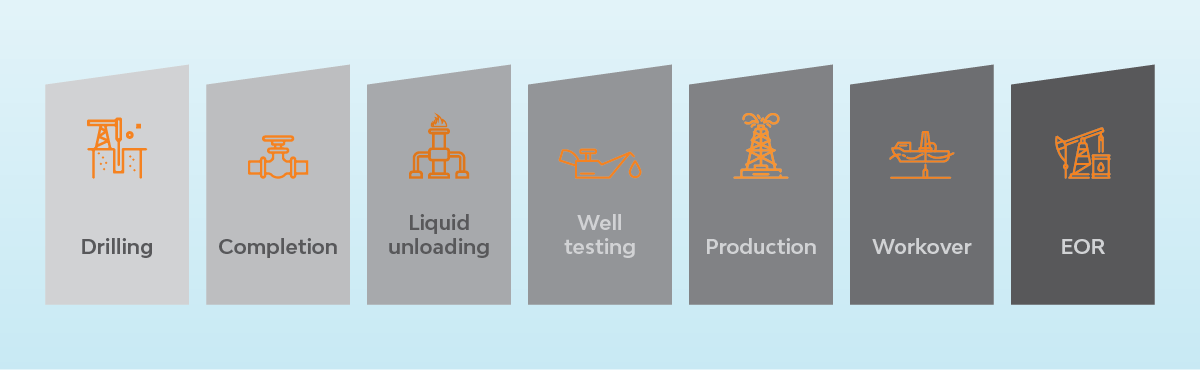
Upstream
Emissions from production and processing operations are higher here compared to the midstream. About five to 37 percent of emissions are from upstream, compared to the rest of the life cycle.
The following upstream activities are significant contributors to emissions:
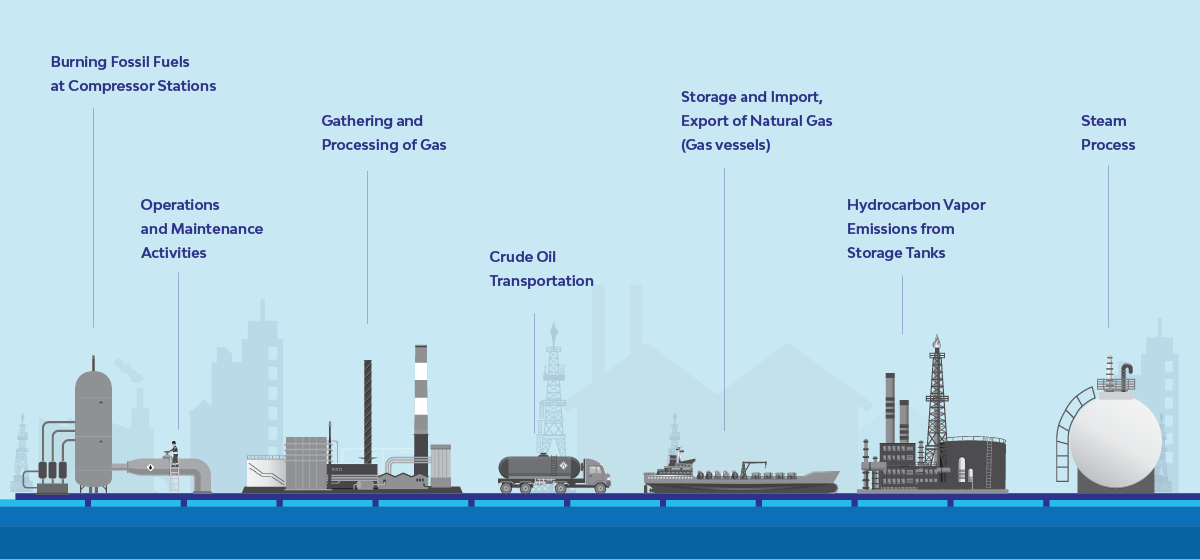
Midstream
There are lower emissions here than in the upstream and downstream industry. The following activities contribute to GHG emissions:
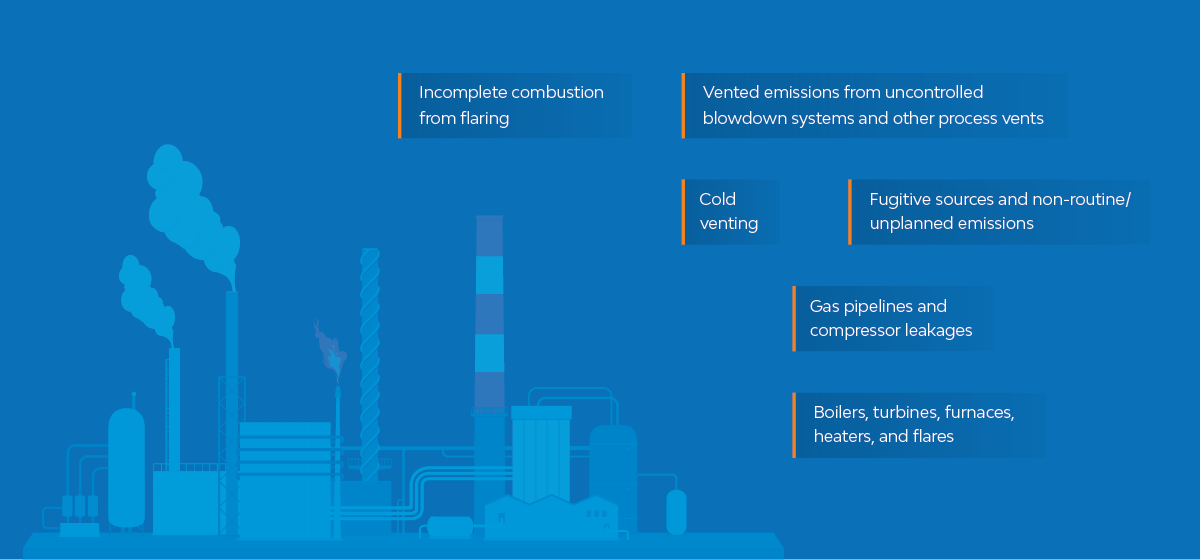
Downstream
Methane emissions from downstream operations are significantly higher than the rest of the operations. They arise from:
Decarbonization potential in the Oil and Gas industry
Oil and gas companies have set ambitious goals to achieve Net-Zero, taking numerous measures to reduce GHG emissions. These can be broadly categorized into two approaches. One is to shift to carbon-neutral or low carbon energy sources such as wind and solar energy, green/blue hydrogen, etc. However, reducing GHG emissions from upstream, midstream, and downstream operations is easier and faster.
In traditional oil and gas businesses, existing operations throughout the oil and gas value chain are well established, decades old, and have already built the infrastructure. However, a little fine-tuning in operations, processes, maintenance routines, and infrastructure, along with a selection of the right digital technology, can reduce the carbon/methane footprint to a great extent.
The following measures are the most beneficial to lowering carbon intensity from the existing operations:
- Flare reduction
- Greener feedstocks
- Reducing fugitive emissions
- CCUS
- Electrification of equipment
- Robust leak detection measures
- Predictive maintenance and reliability operations
LTIMindtree’s digital offerings to accelerate the Net-Zero journey
The oil and gas industry is constantly under pressure to reduce GHG emissions while meeting increased energy demand. This situation calls for more robust and practical solutions to measure emissions and help oil and gas companies reduce emissions quickly and efficiently.
While companies are planning various initiatives for decarbonizing their operations, digital technology will significantly reduce the overall carbon footprint through real-time measurement and control of GHG emissions.
LTIMindtree is committed to solving for society with decarbonization
Leveraging our experience of serving the oil and gas industry for the last two decades, we at LTIMindtree have taken a broader approach to solve decarbonization.
We bring overarching digital solutions, a global partner network, industry experts, and a wide range of services to help our clients manage overall GHG emissions and lower the carbon intensity of their operations.
Our solutions and offerings in this area go beyond a traditional IT-centric approach to provide end-to-end supporting infrastructure solutions. These solutions are aligned with industry initiatives for lowering emissions through existing operations.
| Sr. No. | Solution | Brief about solution |
| 1 | Emissions Management and Optimization Solution | Solution for end-to-end management and tracking of Scope 1,2 and 3 GHG emissions throughout business processes across all industry segments. |
| 2 | ESG Reporting | Digital solutions and services for everything needed to make ESG reporting better, faster, and affordable. |
| 3 | Integrated Energy Efficiency Dashboard | Fully integrated solution to track and plan energy utilization from operations and plan for efficient energy management strategies. |
Traditional oil and gas companies must embrace change, plan for decarbonization in the true sense, adapt the right digital technologies to stay competitive—and achieve carbon neutrality.
Reducing scope 1 and 2 emissions is the first focus for many organizations; however, scope 3 plays a significant role in their total emission for a few industry segments. Since scope 3 emissions control involves collaboration with multiple entities outside the organization, choosing the right technology is even more critical.
Most oil and gas companies have already built digital twins of their oil fields, equipment, pipelines, and refineries. This is the right time to leverage this investment and utilize those digital twins to represent the GHG emissions too.
There are multiple platforms/products available in the market to solve decarbonization challenges. However, companies are facing issues even after investing in the products. Most of the products available in the market are intelligent enough to process ESG data and draw analytics only after the data is brought inside the platform/product*. However, this is where the challenge lies. For most companies, ESG-related information is not readily available; it is not in a shape and form that can be fed directly to the selected platform/product. It needs a lot of due diligence to identify suitable data sources and convert them from raw data to a usable format.
LTIMindtree brings the entire ecosystem, including infrastructure, consulting, digital solutions, and system integration services, to solve these issues.
References
Source: McKinsey & Company Report (The future is now- How oil and gas companies can decarbonize)
Data Source: https://carnegieendowment.org/?lang=en
Latest Blogs
Introduction What if training powerful AI models didn’t have to be slow, expensive, or data-hungry?…
Pharmaceutical marketing has evolved significantly with digital platforms, but strict regulations…
Leveraging the right cloud technology with appropriate strategies can lead to significant cost…
Introduction The financial industry drives the global economy, but its exposure to risks has…




