Characteristics of an Assembly Line Control
Manufacturers today are compelled to deliver high quality products and services at a reasonable price, due to increasing customer expectations. Thus, they need to employ various techniques to ensure that the product manufactured is highly reliable. This is done by performing burn-in tests or satisfy the customer by offering different types of warranties.
If any problem arises when the customer starts using the product, then there is high cost associated with it. Warranty and related problems have traditionally been considered a necessary evil for conducting successful business. With manufacturers spending approx. 0.5% to 7% of annual revenues on warranty, the total spend in the US alone stands at $23 billion. Globally, this number is believed to be about $70 billion, equal to the GDP of some small countries. This is because there might be recall of the product, and even after spending this amount of money, the real cause of the defect is unknown.
There is a great opportunity to reduce “detection to remediation” time through an effective tracking of the product when it is assembled. This tracking is achieved by storing the data during process which can be recalled if any problem arises, and root cause of the issue can be known. This is made possible through a very effective and robust assembly line control application. Apart from proper tracking, an assembly line control serves other purpose too.
There are various process to manufacture a car which requires a system to ensure trouble-free interlinking of the countless different process step, where a large number of data record is exchanged between various stations of the process chain. This creates a large database, which needs to be collated, processed and evaluated during production, and sent to the different controls, drives and sensors to ensure that the right car, with the right paintwork finish and equipment package, rolls off the line at the end. From this database, analysis can be made to identify bottlenecks and the cause of failure, which optimizes the process, and in turn increases the production volume. In the end, an increase profitability that is desired by every company. Any Assembly Line Control application will have following key modules:
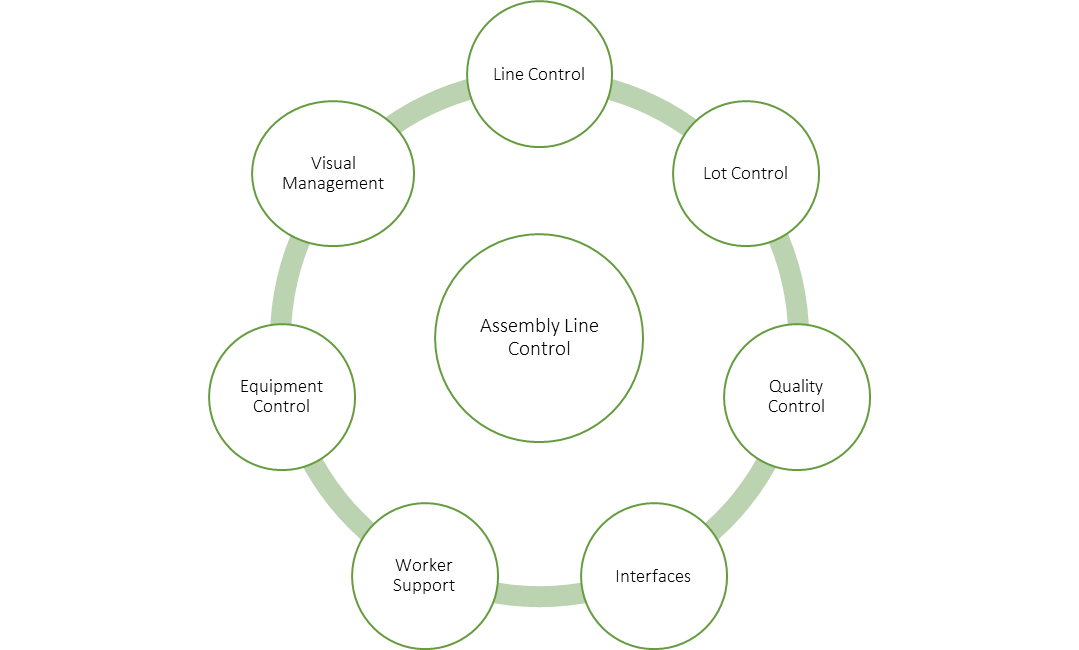
An Assembly Line Control will be able to cater to multiple product types. For an automotive assembly few examples of products are – Frames, Engines, Heads, Blocks, Knuckles, Plastic Parts, IPUs, etc.
Line Control
- Proper sequencing of the production process to manage what and when the product should be built
- Manage what and when a product should be built and track when it was actually built
- Track where the product is currently located
- The available time and reports the throughput of the line based, on which the next schedule is prepared
- Track the output of each station and plan it according for next station ensure to keep buffer inventor
- Find what the inventory was as of a specific point in time
- Collect how long it took to process a particular product
Lot Control
The model and options variety in automobile production requires flexible manufacturing, optimal sequencing and individual allocation of parts and components. The challenge is to deliver the correct individual automotive parts to every workstation in the production line, and that in the exact sequence in which the vehicles are being assembled on the production line. If a necessary component is not supplied in time, the pre- planned work sequence of all subsequent workstation in the production line has to be changed accordingly. This problem is been taken care by this module, which ensures that correct part reaches the correct workstation. This module comes with the following features:
- Data collection and validations like torque test, oil leakage test, etc.
- Verify and track allocation of parts from a lot to a product
- Enable wireless torque controller based on proximity to product
- Verify and track history of part serial numbers to product
- Verify and track history of measurements to product
Quality Control
Performance and product issues can be discouraging to customers, and a detriment to the brand. Having a product recall or other issues can create dissatisfied customers. But these types of issues can be resolved by having a system to detect and track defects, while the production is on. Few key features of this module are:
- Defect detection, record and submit the real-time defect images in the database
- Repair the defects
- Tracking Repair vehicle through Repair areas
- Input defects from external devices like LETs, Headless stations and tracking them within the system
- Check product state for missing/bad installed parts, Not Repaired defects, failed LET tests, Current tracking status, etc.
- Manage linkage of incidents to root causes and effectiveness of counter measures
Interfaces
An Assembly Line Control will exchange and manipulate data with multiple systems and sub systems i.e. Production Control Systems, Consolidation Center, Sales, Distribution Center, Warranty systems, Manpower Management System, Manufacturing Work Instruction Management System, etc.
- Production Planning: It is necessary to satisfy customer’s demand by proper utilization and allocation of production resources. It generates planned production orders, based on the forecasted time-phased demand, in respective monthly / weekly time buckets. After confirmation, full functional production orders, with adjustable routing and components, states what quantity of product should be manufactured and its scheduled date of production. While generating the production order, the system takes cognizance of the number of hours needed for the order and capacity of machines and work centres, and availability of materials and components.
- Sales: This module allows a company to (re) organize and track the sales process in an efficient way, which includes:
- Tracking of each customer orders right from placing an order to dispatch of material for that particular order and customer.
- Automating the sales force activities such as visits to customers, expenses, and competitor assessment is possible with this module.
- Many a time’s payments have to be received from customers after dispatches are made. With this module, executives can contact customers and follow-up each and every sales invoice and receive payments for such invoices.
- It also has features to track lost orders and identify the reasons for loosing those orders.
- It also helps to prepare reports to track sales trends over different periods, drill down for the consolidated data, allow for sales forecast and give a bird’s eye view of the sales and marketing activities of the company.
- Distribution Center:
- It is designed to track the activities performed in distribution center.
- It automates the process of receiving, managing and shipping goods to customer.
- Keeps track of the inventory with its specific location
- It also removes the risk of stock pile-up, stock outs, pending orders and loss of sales due to customer dissatisfaction.
- Warranty Management System: It provides a one-stop solution to all your warranty process-related problems – from contract/claims administration to reporting.
- It entails monitoring of policies, flat rates, fault codes, rules management, registration, and claims processing
- Support for multiple warranty types including OEM, product and third party
- User-defined business rules to automate charge- back procedures
- Query according to customer, serial number, date, type, product and region
- Track service calls under warranty, total warranty cost, and in-warranty product returns
- Track asset history, revisions, readings, location, PMs and configuration
- Manpower Management System:
- It is designed to track and manage manpower on the shop floor
- It manages the skills of the resources, process trainings and planning resources for a day, shift and process
- Manufacturing Work Instruction Management System:
- It is designed to define manufacturing work instructions based on Plant, Department, Line, Production Rate and Vehicle Model Code
- It allows to create processes and associated units of instruction
- Each unit of Instruction can have parts, which need to be installed and associated torque and part mask values
Worker Support
- Generate work instructions for worker to follow during assembly at each station, and assist associate by instructing and verifying with pictures and words the sequence or process of assembling parts with tools.
- Assemble the desired part to the desired product, without any error by printing parts marks for products.
- Inform associates of production sequence, lot and model changes.
- Play sounds/alarms to inform workers about exceptions or derive attention of Team Leaders in areas affected.
Equipment Control
- Monitoring proper functioning of tools and associated equipment’s.
- Send data to and collect results from equipment like Torque Controllers, PLCs, Laser Etchers, Immobi, LETs and Thermal Printers, etc.
- Collecting data for permissible limits of equipment’s, and store in a database in case there are any liability issues.
Visual Management
- Shows the current status to anyone that stands and observes, it may be production status, delivery status or machine status.
- Performance, trends, and alarms for reporting, analysis, and continuous improvement are also visible.
- Improve the speed of reacting to line stops by visualizing equipment alarms.
- Send alerts or notifications for missing configurations, not repaired defects, equipment alarms, station errors, etc to signboards and mobile devices.
Latest Blogs
Core banking platforms like Temenos Transact, FIS® Systematics, Fiserv DNA, Thought Machine,…
We are at a turning point for healthcare. The complexity of healthcare systems, strict regulations,…
Clinical trials evaluate the efficacy and safety of a new drug before it comes into the market.…
Introduction In the upstream oil and gas industry, drilling each well is a high-cost, high-risk…




