Business Leaders and Data Experts Tackle ESG Data Challenges—ESG as a business driver, insights into ESG data strategy
Welcome back to the second blog in our series on ESG data challenges and the ESG strategy framework. I look forward to sharing further insights from a recent roundtable meeting in OIso with industry experts and veterans in data analytics and strategy. Previously, we have focused on the framework of the financial sector and the need for a robust ecosystem for ESG data collection, calculation rules, and reporting services to ensure the accuracy of carbon footprint measurements.
Here’s an infographic that covers my insights in a nutshell on mastering the six steps to shape your ESG data strategy. Click here to download.

At the heart of ESG lies a data challenge. You gain better access to data, better solutions, and improved compliance with a well-crafted data strategy. In this blog, we will dive into the business drivers and provide insights into the data strategy defined during the delegates’ insightful discussions in the evening in snowy Oslo.
Key business catalysts
In setting the scene for the evening, we offered insights into the primary factors driving the prioritization of ESG activities. We discussed the significance of incorporating them into the annual report.
Why businesses care!
- Forward-thinking companies view ESG as an opportunity to enhance company value and foster growth while positively impacting the environment.
- Companies are compelled by regulations and directives from the EU, aiming to avoid potential fines or fees, such as in the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive.
- Meet customers’ environmental expectations to stay relevant.
- Sustainability is considered a cost-saving activity.
- Keep, attract, and retain new talent.
- Gain climate-tech venture capital funding – a new economic.
These are the key arguments we are met with when we engage in ESG projects with clients.
What is ESG data?
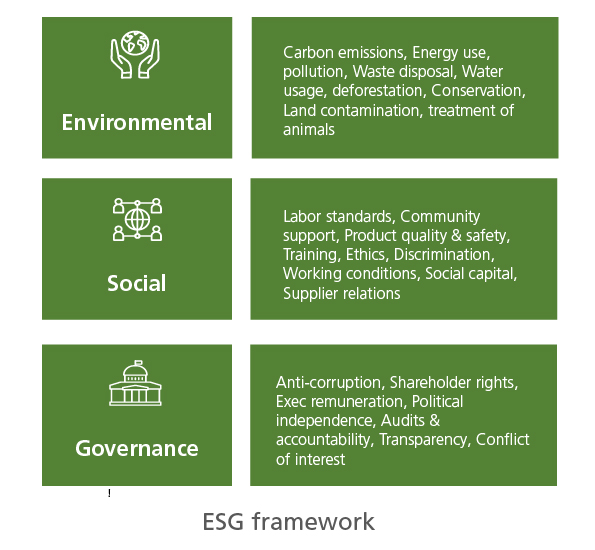
Before diving into the evening discussion, we briefly covered the ESG framework initially defined by the UN. This framework provides a structure for assessing specific performance criteria, as listed in the figure.
The delegates were encouraged to cover various aspects of ESG data strategy, including how to collect, curate, and publish results to relevant stakeholders in the organization. This includes critical considerations businesses must consider when measuring and reporting carbon emissions, including the complexity of the value chain.
Defining an ESG data strategy
Upon revisiting our evening discussion, it’s evident that a successful ESG data strategy requires a holistic approach, seamlessly incorporating ESG factors into all facets of the data strategy.
Per our discussion, any data strategy must address these eight key elements.
- Define ESG goals and objectives: Identify the key ESG areas that align with your organization’s mission and vision. These could range from reducing carbon footprint to improving worker safety or ensuring fair corporate governance – as described in the ESG framework.
- Identify relevant data sources: Determine where to collect the necessary data to measure progress towards your ESG goals. These could include internal sources like operations data and external sources such as government databases, power plants, or third-party ESG ratings.
- Data collection and integration: Establish processes for gathering and integrating ESG data into a centralized cloud platform. This may involve developing new tools or leveraging existing data management platforms.
- Data quality assurance: Implement measures to ensure the accuracy and consistency of your ESG data. This could involve periodic data audits, validation checks, or AI and machine learning for anomaly detection.
- Audit-ready ESG data: The regulators will expect companies to have the same level of controls as they do on financial reporting for Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) Reporting. This means that companies must ensure they have “audit-ready” ESG Data.
- Data lineage and transparency: To develop a better understanding of the data, enterprises need to clarify the availability, ownership, security, and quality of the data as it flows across the organization. They also must demonstrate where the data originated, trace its journey through the systems in the organization, and show how it changed along the way.
- Analysis and reporting: Analyze the collected data to gain insights into your ESG performance. Develop clear and concise reports for stakeholders, including employees, investors, and regulators.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly review and update your data strategy to reflect evolving ESG goals and standards. Use feedback from stakeholders and lessons learned from previous reports to guide improvements.
- Data security and privacy: Ensure that all ESG data collection and storage practices comply with relevant privacy regulations and security best practices.
- Stakeholder engagement: Actively engage with all stakeholders, including employees, customers, partners, and investors, to understand their ESG expectations and to communicate your ESG initiatives effectively.
At the heart of ESG lies a data challenge that deserves a well-crafted data strategy. Improving data access leads to enhanced solutions and ESG reporting. By implementing sound methodologies for data measurement, effective management becomes achievable.
Walking the talk
I left the roundtable with the understanding that ESG data projects is not a solo effort, but a collective effort that requires robust business support—it should be considered as a team sport with top management priority. It’s not only an IT problem but also a close collaboration between business experts and data professionals. The primary goal is to obtain reliable and precise metrics promptly.
Establishing a fully managed, scalable, and flexible data platform for ESG workloads is essential. This platform will accelerate the organization’s data initiatives by providing low-latency and cost-effective data management. By setting this up from the outset, most of the effort can be concentrated on achieving business objectives, enabling contributors to transform business requirements and rules into tangible code and deliver the requested data artifacts.
Once the core data platform is in place, it’s recommended to approach ESG metric development in an iterative or circular model. This involves creating each ESG metric one at a time, establishing an end-to-end “data pipeline,” then reevaluating initial assumptions and adjusting as necessary. The knowledge gained from this process will accelerate the creation of subsequent metrics, promoting continuous improvement.
ESG projects can also drive impactful changes within a company’s internal processes. In some instances, these initiatives can even lead to cost savings, benefiting the organization’s bottom line through less fuel usage, greener energy, or improved return goods service.
Events like the Oslo roundtable play an essential role in shaping the future of ESG data strategy by staying updated on modern ESG platforms, data integration, and advanced pipelines where business rules can be applied to secure carbon footprint figures.
Explore more here:
LTIMindtree: Enterprise ESG Strategy with Snowflake
LTIMindtree’s Manufacturing NxT, built on Snowflake Manufacturing Cloud
LTIMindtree’s ESG & Sustainability Tech Consulting
LTIMindtree’s ESG Consulting Services and Digital Offerings video
Snowflake: Telecoms Reduce Carbon Emissions with Generative AI
Snowflake: Snowflake Enables Cargill’s Goal to Achieve Zero Carbon Shipping
Snowflake: Scania Uses Data Mesh and Snowflake’s Data Cloud to Drive Transport Sustainability
Snowflake: Data Sharing Is Caring: Driving Sustainability with Data
Snowflake: Demo of how ESG Data is incorporated into a Financial Services workflow
Snowflake: How to build an efficient enterprise ESG data strategy in banking with machine learning
Snowflake: Natwest transforms its ESG analytics and data culture
Snowflake demo: incorporating ESG into portfolio construction
More from Tom Christensen
Leveraging the right cloud technology with appropriate strategies can lead to significant cost…
It pays to be data driven. Research conducted by Forrester1 reveals that companies advanced…
Welcome to our discussion on responsible AI —a transformative subject that is reshaping technology’s…
At our recent roundtable event in Copenhagen, we hosted engaging discussions on accelerating…
Latest Blogs
Core banking platforms like Temenos Transact, FIS® Systematics, Fiserv DNA, Thought Machine,…
We are at a turning point for healthcare. The complexity of healthcare systems, strict regulations,…
Clinical trials evaluate the efficacy and safety of a new drug before it comes into the market.…
Introduction In the upstream oil and gas industry, drilling each well is a high-cost, high-risk…




