AI in IT as AIOps
As the world is switching to digital ways of working, application architecture is becoming more complex, making IT operations and process handling challenging. Introducing AI in IT operations (ITOps) increases efficiency, reduces operational complexity, accelerates remediation, and improves user experience. A report by Allied Market Research proves that incorporating AI in IT operations (AIOps) is a growing trend. The report projects a CAGR of 37.90% in the global AIOps market size from 2021 to 2030 (from USD 26.33 billion in 2020 to USD 644.96 billion by 2030).
ITOPs vs. AIOPs
IT Operations are processes defined and followed by an organization to manage its IT infrastructure, which includes servers, network devices, software, applications, etc. They are based on frameworks like ITIL, which define standards, set of procedures, and best practices in digital service management. With the rising need for technology adoption across all industry sectors, IT service providers face problems like a high volume of incidents, demand for high availability of business, and increased resolution time.
What is AIOps?
Artificial intelligence in IT Operations (AIOps) uses AI in IT operations by leveraging data and technology such as machine learning, reinforcement learning, etc. It expedites IT services by helping analyze the dependencies of problems faster and predicting issues. This allows IT service providers to deliver faster and smarter by reducing the mean time to repair.
It is unlikely that AI will replace engineers at their jobs. Instead, it has been helping with speeding up and automating mundane and repetitive tasks and controlling quality. AI also allows engineers to focus on more complex problems and strategic areas. Intelligence that capacitates bots is the simulation of human intelligence by machines.
AIOPs in the market
In today’s market, some of the areas of IT services where AI is evolving are –
- Event correlation
- Noise reduction
- Anomaly detection
- Predictive analytics
- Proactive analytics
- Contextualization
- Root cause detection
- Recommendation
AI Operation (AIOPS) is set up in three phases in IT Operations Management (ITOM). In phase one, data is collected in volume, variety, and velocity. In phase two, the observed data is processed in an AI bot for anomaly detection, correlation, contextualization, historical analysis, etc. Phase three involves post-analysis actions, wherein bots give recommendations and trigger automation in IT Operations.
Placement of AI bots in an IT environment
Data plays a crucial role in providing intelligence to bots. There are multiple ways of gathering data in ITOps. The placement of data-collecting bots is decided based on the use case of the AI solution.
- The first method involves gathering data directly from servers and applications where business operations take place. This method requires a data collector bot to extract the necessary data from configured machines. The data collected can be telemetry, metrics, logs, and events. The advantage of this method is that any relevant data to train AI bots can be extracted and transferred in the desired format. For example, checking the availability of servers and data points like CPU, memory, and storage usage patterns is essential to predict deadlock situations of a system going down. This data can be gathered from the OS of the respective server and loaded into the bot to analyze the usage pattern. Post the bot analysis, IT engineers can be warned proactively whenever a machine-critical activity occurs.
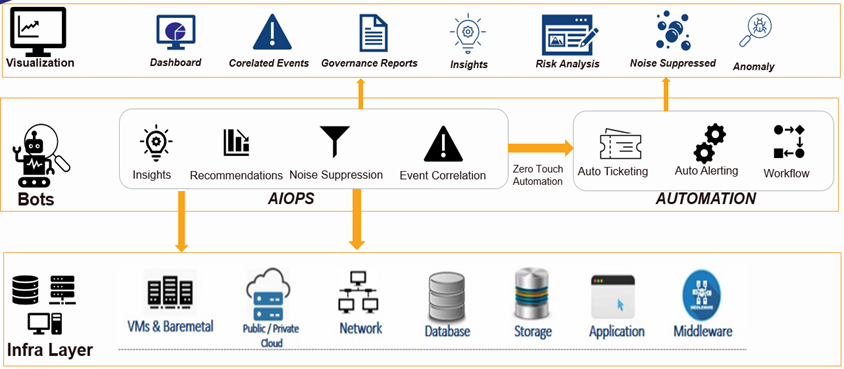
Figure 1: Bot placement in infra
- The second method is to overcome the disadvantages of what AIOps tools or firms are facing today. In most businesses, clients do not consent to placing bots or data collection agents directly on the servers. The constraints are because of data privacy policies and other such factors. Another option is to collect data from existing tools used in IT operations. They could be ITSM tools like ServiceNow, BMC Remedy, etc., ESM Tools like SolarWinds, Nagios, New Relic, and APM tools like Dynatrace. All these tools are defaults, installed to run IT services and manage businesses. AI bots can be placed behind them for connecting and collecting data from existing tools. Implementing an AIOps platform as a standalone solution instead of AI bots reduces the repetitive effort spent building tool plugins. Such a platform should also have AI/ML frameworks for easy onboarding and releasing of ML models to enable more intelligence in operations.
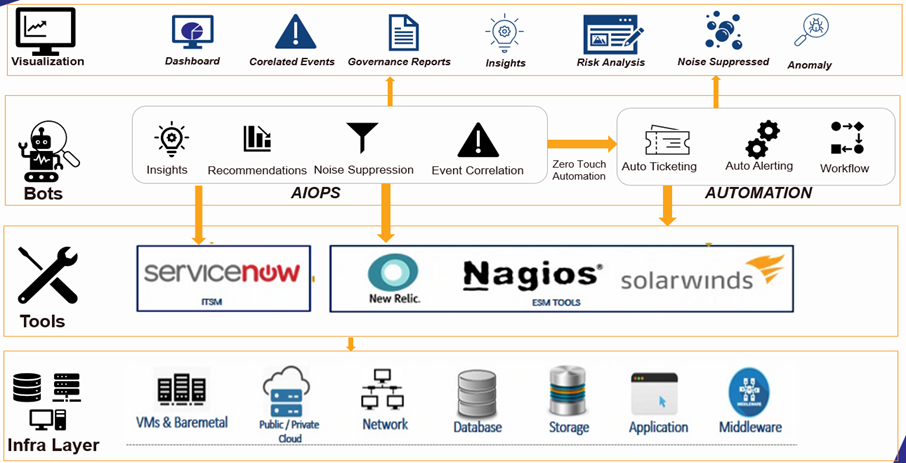
Figure 2: Bot placement behind tools
AIOps platforms should be capable of
- Observing different types of data from multiple sources
- Engaging with data, analyzing operations with data collected
- Taking actions with the built-in orchestrating feature or by connecting to external orchestrator tools
Introducing the AIOps platform in the infrastructure takes care of data consolidation and IT infrastructure management through a single window.
Automation in AIOps
In IT operations, AI is now used to eliminate issues proactively and reactively after analyzing data points. So, how do we enable automation with AI in IT operations?
Automation, whether a workflow or a runbook, needs a trigger point. AI can be integrated as a trigger point for automation. This is called zero-touch automation. For example, AI installed to monitor a server’s availability detects a steady increase in CPU and memory usage. A bot analyzes and validates that it is because of long-running daemon processes. With zero-touch automation in place, an automation flow is called to terminate the daemon process to ensure server availability.
The era of AIOps
Building AIOps is a continuous process and more challenging than involving humans in ITOps. There are two methods of bringing AI into operation. It is essential to identify potential use cases, which can be –
- Pragmatic use cases – These ideas are technically feasible and viable for the business and can create an impact in a short span.
- Aspirational use cases – These ideas might not be technically feasible or viable for the business currently but can potentially create a significant impact in the long run.
In the process of developing solution ideas for any use case, an AIOps engineer plays a vital role. The engineer, as an ITOPs stakeholder, identifies the problem statement and, as a solution architect, designs the solution. Further, as a data engineer, s/he builds data collectors and pipelines, and finally, as an AI and ML engineer, s/he works on algorithms to create ML bot solutions. Throughout the journey, it is the duty of the developer to build responsible AI with fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Latest Blogs
A closer look at Kimi K2 Thinking, an open agentic model that pushes autonomy, security, and…
We live in an era where data drives every strategic shift, fuels every decision, and informs…
The Evolution of Third-Party Risk: When Trust Meets Technology Not long ago, third-party risk…
Today, media and entertainment are changing quickly. The combination of artificial intelligence,…




