A Paradigm Shift in Customer Service with Generative AI (GenAI) – Making ‘Intelligent’ Chatbots to Enhance Customer Support
‘Language Models (LMs)’ in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) are not new. However, the abilities of Large Language Model (LLM)-based chatbots, such as ChatGPT, are significant as evidenced by the adoption of ChatGPT since in November 2022. ChatGPT is an open-domain LLM-based chatbot that contains around 175 billion parameters. It was trained over an immense text corpus spanning almost the entire internet. As a result, it can generate fluent, grammatically, and syntactically correct text that is consistent with the input prompt.
LLM-based chatbots (such as ChatGPT) are a pioneering example of the potential that generative AI offers in customer service automation. While they represent a significant departure from traditional approaches, it is crucial to understand their capabilities, training methodologies, and limitations when compared with human-like conversational capabilities to enhance customer service. The diagram below depicts the capability range of human and chatbot for various tasks and interactions.
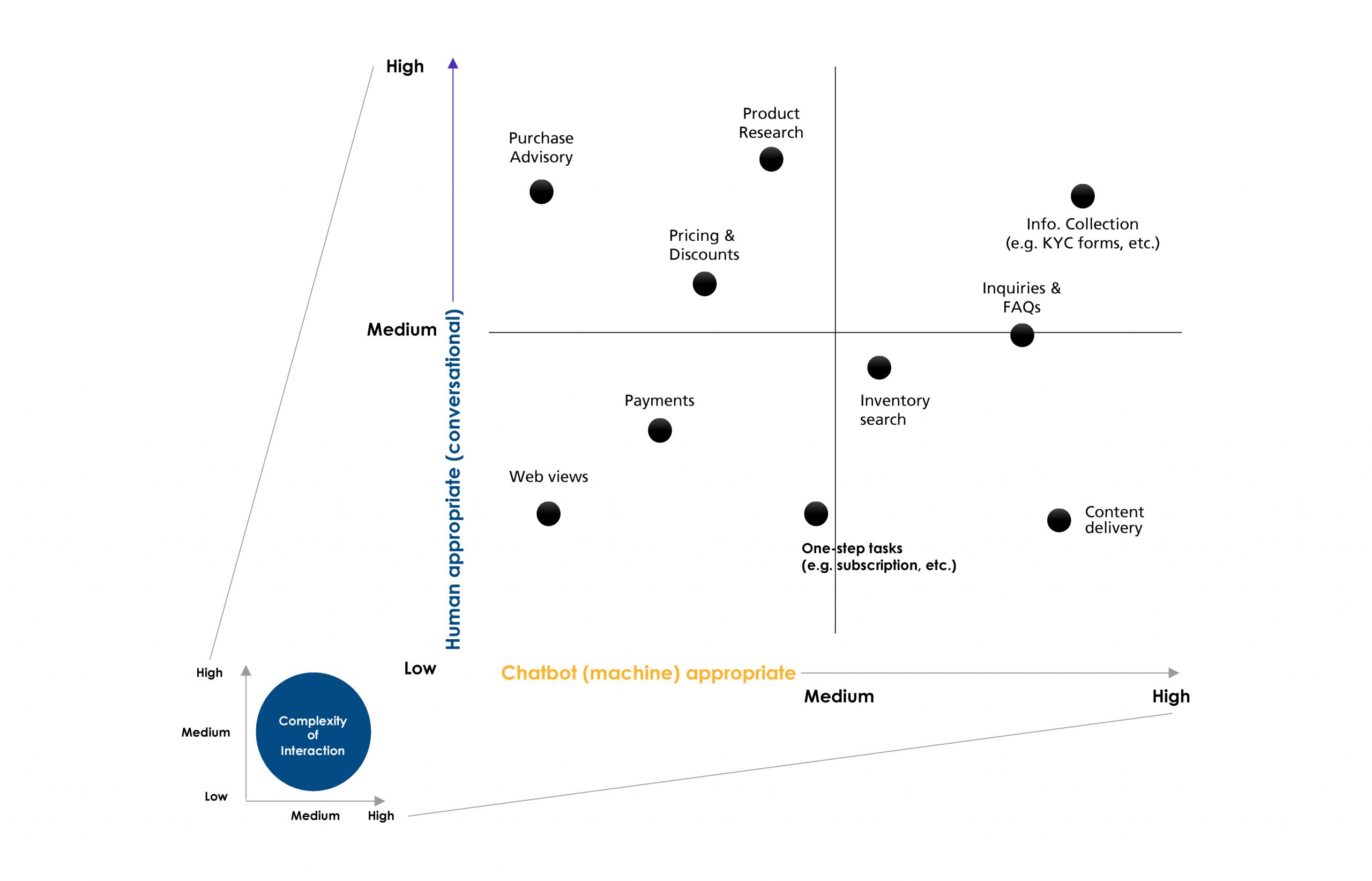
Figure 1: Complexity of human (conversational) and machine (chatbot) interactions
In this blog, we will explore the transformative potential of generative AI-based chatbots (such as ChatGPT) in augmenting customer service operations, focusing on their role as Large Language Models (LLMs) and their integration into task-oriented chatbots for the customer support function to provide ‘intelligent’ and ‘human-like’ conversational support to customer inquiries
AI chatbots have been experimented with for quite some time now. With the latest technological advancements and the advent of business-specific use cases, AI chatbots have become more sophisticated and are being used by many organizations to automate their business processes and provide a better customer experience. However, there is more to be done than said!
Let’s explore chatbots potential in more detail citing ChatGPT as an example.
ChatGPT and language models
At its core, ChatGPT operates as a Language Model (LM) within the realm of Natural Language Processing (NLP). LMs, which are not a recent invention, lay the groundwork for ChatGPT’s functionality by assigning probabilities to words based on context. Trained on a vast corpus of internet data, ChatGPT analyses input prompts and conversation history to generate contextually relevant responses.
Open domain vs. task-oriented chatbots
While LLM-based chatbots (such as ChatGPT) excel in open-domain conversations, their true potential lies in their integration into task-oriented chatbots. Unlike open-domain chatbots, which engage broadly across topics, task-oriented chatbots focus on specific use cases, such as booking appointments, handling customer inquiries, order cancellations and returns, etc. By leveraging this generative AI-based capability within task-oriented frameworks, organizations can streamline customer service processes and enhance user experiences.
Strengths and limitations of LLMs
Standalone LLM-based chatbots (such as ChatGPT) offer impressive language generation capabilities, and thereby significant advantages, particularly in open-domain contexts. ChatGPT’s ability to generate fluent, contextually appropriate text across diverse topics makes it a valuable tool for content creation and customer interactions. However, it is essential to recognize its limitations, including the inability to perform actions beyond generating text and the risk of producing inaccurate responses (hallucinations) due to its probabilistic nature. Most standalone LLMs lack the ability to use third-party tools to produce relevant responses based on the use case. They can only provide answers generated by using information stored in the model parameters from a time-constrained internet snapshot (e.g. the ChatGPT 3.0 model references data till 2021). As a result, it can only provide answers generated by using information stored in its parameters.
Harnessing LLMs for customer service
To maximize the benefits of LLM-based chatbots (such as ChatGPT) in customer service, organizations must adopt a strategic approach that integrates them effectively into existing workflows. Any organization that has Artificial Intelligence (AI) or its subset generative AI in its customer service enhancement roadmap envisions chatbots that perform more complex tasks than just baseline FAQ informational responses to users’ queries. An FAQ chatbot would have limitations as its output is neither personalized nor can it perform tasks to automate business processes and introduce systemic efficiency.
Consider a use case wherein the customer wants to cancel an order. In order that this business process flow is executed from end-to-end by the chatbot, it requires integration with an API (Orders API) with embedded business rules to achieve the desired outcome.
Here is a simple description of steps that must executed by the chatbot in a human-like fashion:
- Request the customer for the Order ID (validate as per business rules).
- Invoke the Orders API to get complete order details.
- Check the order for cancellation (validate as per business rules): Check if the order is already dispatched or if the order was made more than three days ago. Or, if the ordered item belongs to the category={Food, Perishables}. In case any of these business rules are fulfilled, then inform the user that the order cannot be cancelled or returned.
- Else, invoke the Orders API to create a cancellation entry in the database and give all the necessary information to the user to cancel or return the item (as applicable) and get the refund (if already paid).
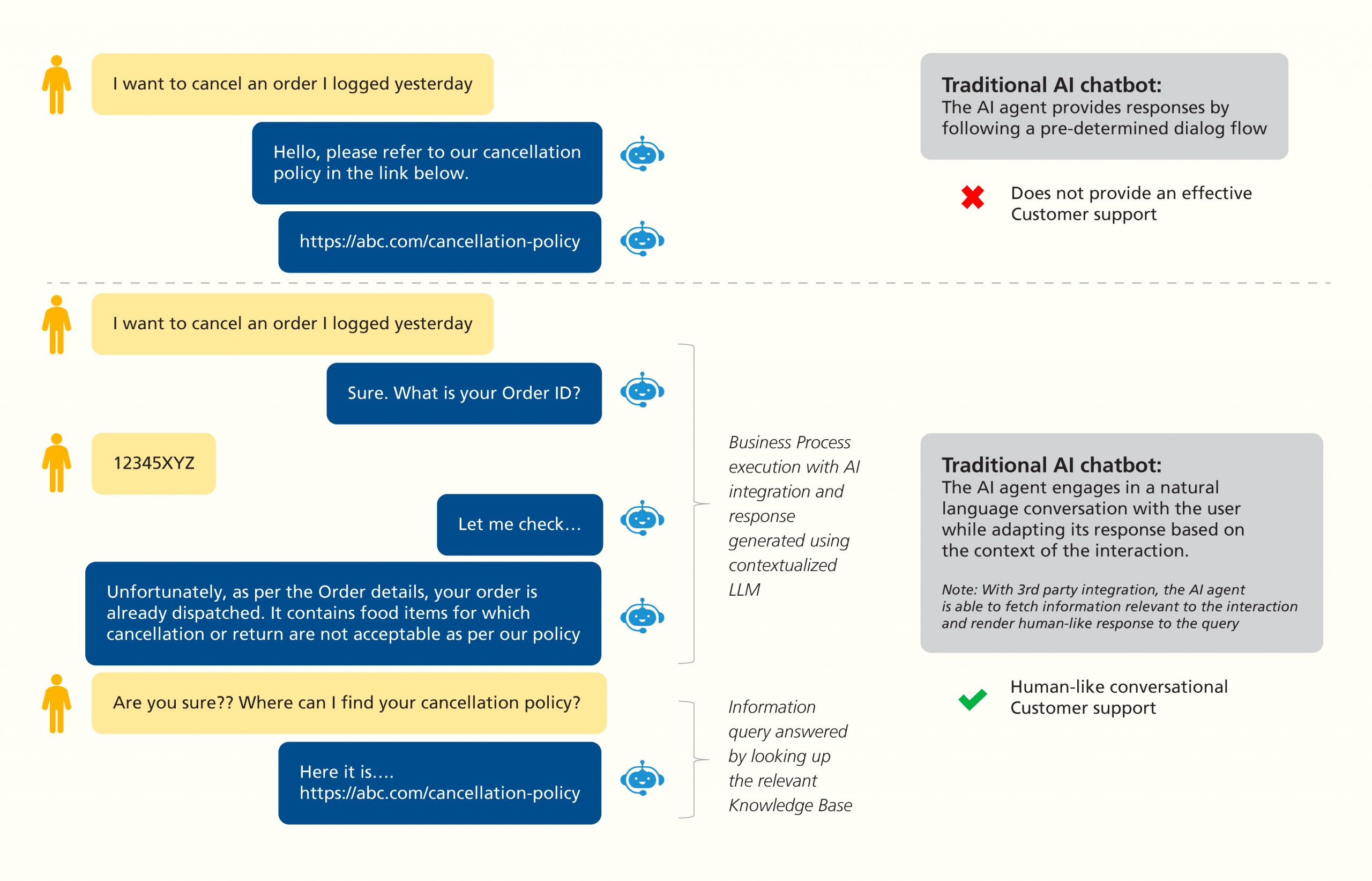
Figure 2: Complexity of human (conversational) and machine (chatbot) interactions
Thus, the idea is to leverage the strengths of a standalone LLM-based chatbot while mitigating its limitations through careful planning and integration strategies.
- Assisting chatbot agent creation: By automating the chatbot agent creation process using unstructured resources like knowledge bases and past chat logs, ChatGPT simplifies the development of task-oriented chatbots. In the above cited use case of “order return”, a simple description would suffice for the dialog flow to be generated automatically by making use of an LLM in the background. Tools like Kore, Auto Builder, etc. can facilitate this process reducing the cost, time and associated manual development efforts.
- Enhancing chatbot functionality: Integrating LLM-based chatbots (like ChatGPT) as a fallback option augments the capabilities of task-oriented chatbots, enabling them to provide contextually relevant responses beyond predefined scenarios. This hybrid approach ensures personalized interactions and improves user satisfaction.
- Supplementing human agents: While LLM-based chatbots cannot replace human agents, they can support them by generating recommended responses and performing micro-tasks such as paraphrasing and summarization. This enhances agent productivity and efficiency, enabling faster resolution of customer inquiries.
Conclusion
Generative AI-based chatbots (such as ChatGPT) represent a paradigm shift in customer service automation, offering immense potential to streamline processes and enhance user experiences. While such chatbots are not a substitute for human intelligence, their integration into task-oriented chatbot agents can significantly boost productivity and efficiency. When used as standalone systems, LLMs lack the ability to provide maximized returns while implementing solutions in the customer service space. However, when integrated into an ecosystem, LLMs hold the potential to revolutionize customer experiences and solve critical business problems.
By harnessing the power of such LLM-based chatbots effectively, organizations can revolutionize their customer service operations and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape.
More from Tushar Sehjpal
According to a 2023 Gartner report1, more than 80% of enterprises will have incorporated generative…
Complex market conditions combined with digitally empowered consumers present a challenging…
We stand at a juncture in the evolution of the internet where the next big step towards the…
Latest Blogs
The energy and anticipation were evident even before entering the arena, and attendees had…
A tectonic shift in wealth is underway, and agility is the key factor that will distinguish…
Educational institutions are at a crossroads where their future hinges on a single question:…
In times of market unpredictability, alternative investments offer a valuable advantage by…




