Introduction
The Payments Services Directive (PSD) is a regulation that aims to modernize the European payments market. It was introduced to enhance consumer protection, promote competition, and foster innovation in the payments industry. PSD2, the second iteration of the directive, came into effect in 2018, bringing significant changes to the way payments are made in Europe. The European Commission concluded that PSD2 is overall successful since its introduction brought significant changes like reduced fraud, enhanced security, boosted innovation, and led to the successful emergence of open banking.

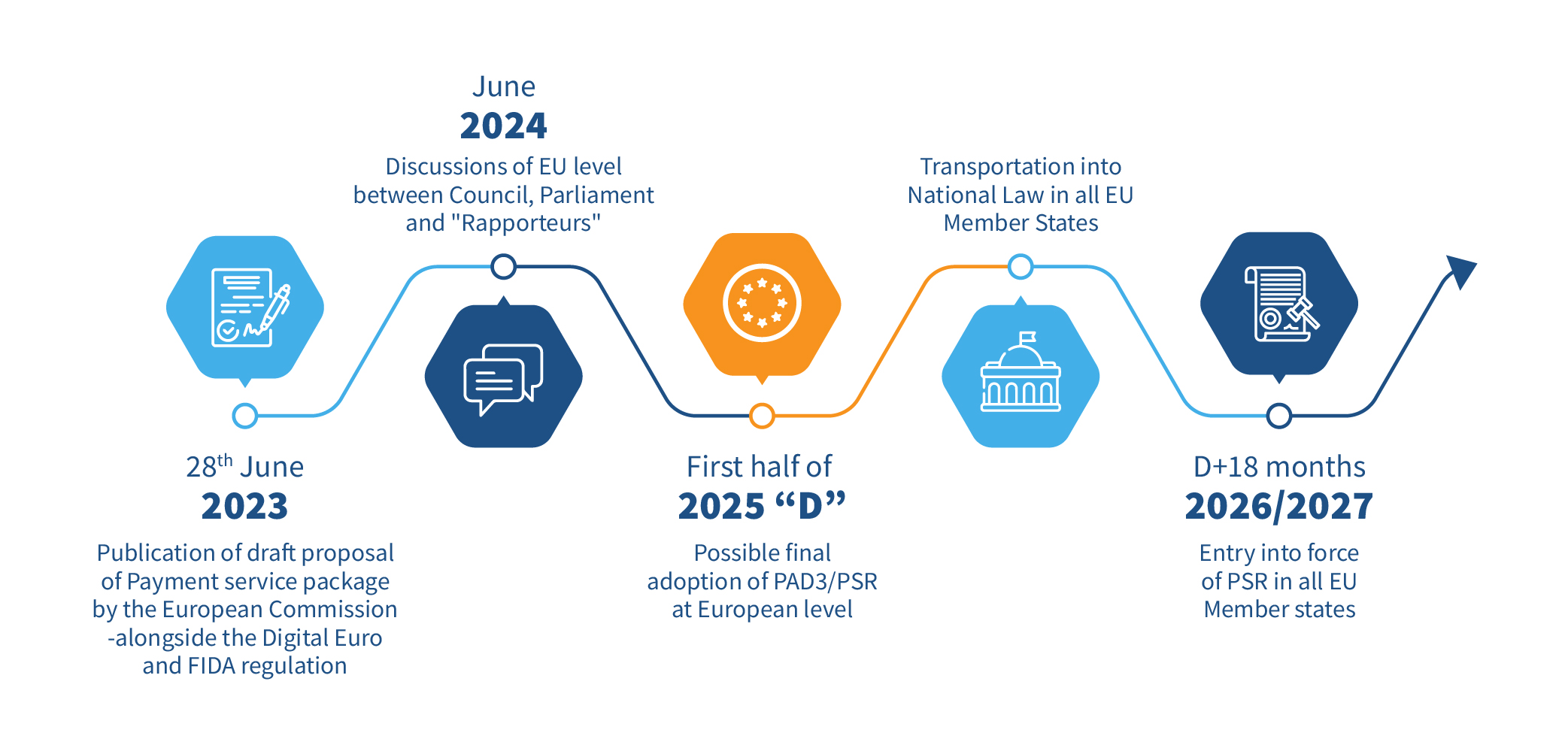
PSD3 and PSR are new proposals from the European Commission to further streamline payment solutions and strengthen the foundation of governance, risk and compliance (GRC) laid by earlier PSDs. They will significantly impact banks, FinTechs, payment service providers, and customers, both from a legal and operational perspective.
PSD3 seeks to enhance competition in the payments sector while defending the rights of customers and their personal data. The focus of PSD3 will primarily be on licensing and the operation of service providers, hence creating a level playing field for non-bank payment suppliers. At the same time, consumer protection and security of transactions will be strengthened, hence aligning the sector with ongoing digital transformations and their associated risks and opportunities.
PSR, on the other hand, seeks to enhance consumer protection, an area where uniformity of regulations is essential. PSR, once ratified and put into effect, will directly affect all EU member states.